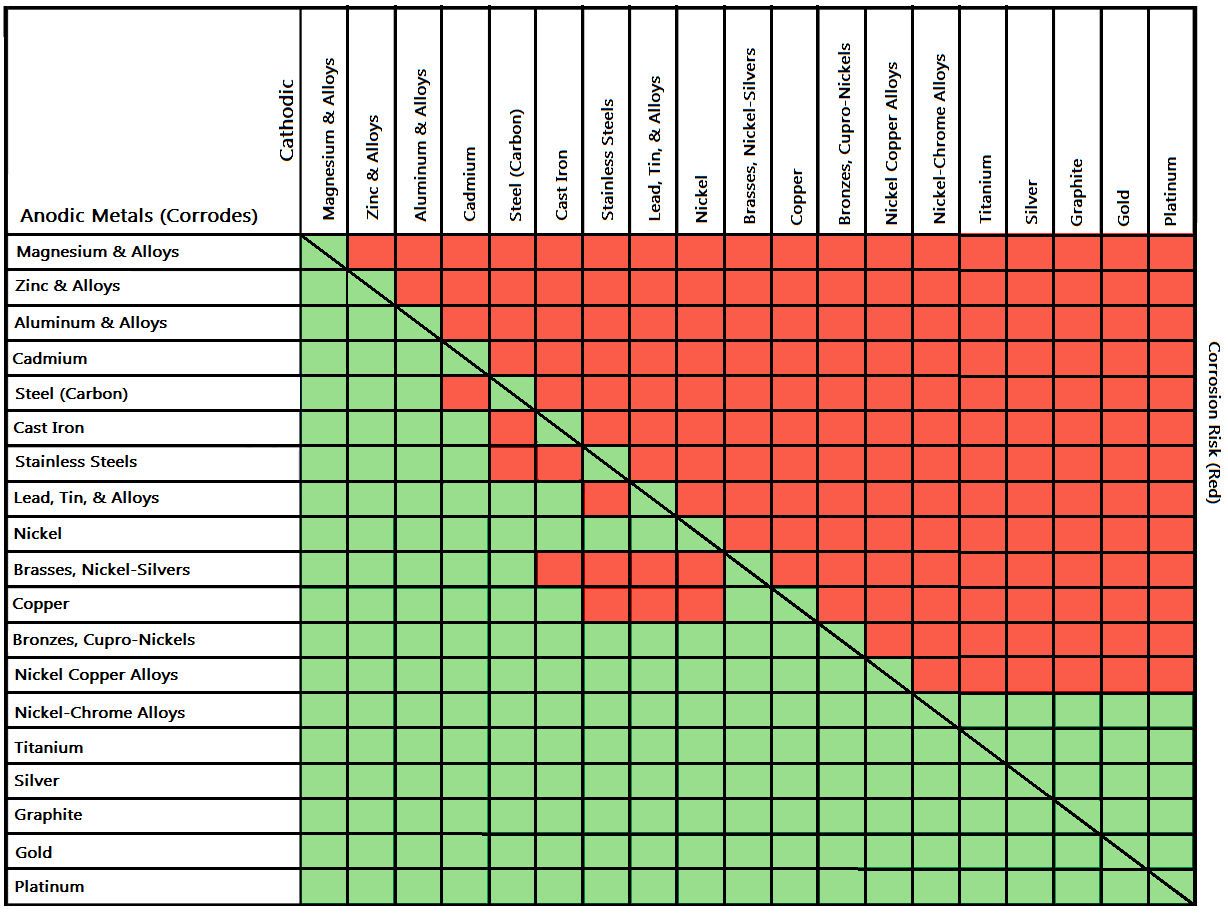
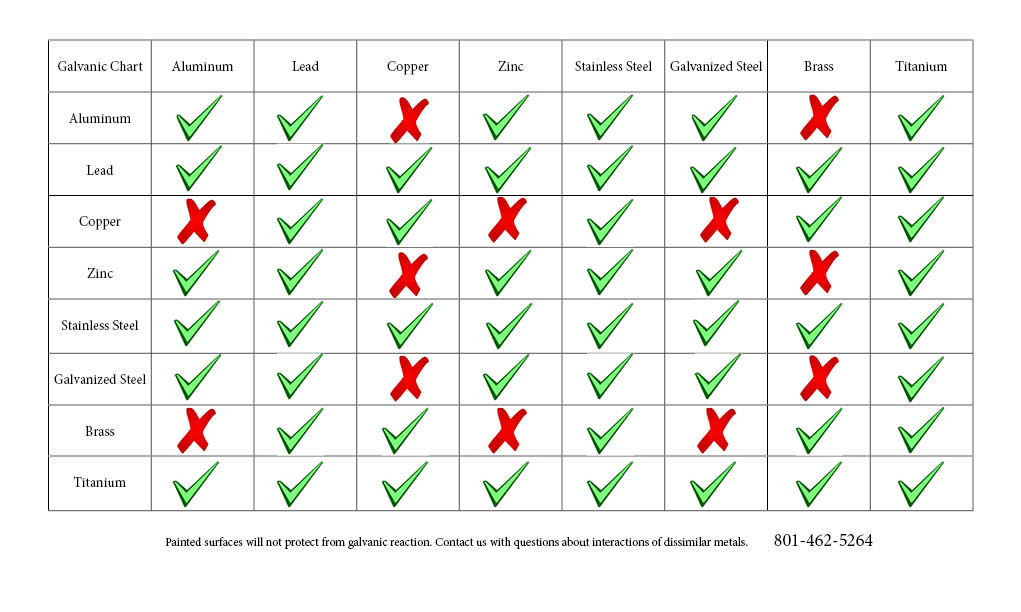
Galvanic Chart Corrosion
Galvanic Chart Corrosion - Zinc coatings on carbon steel and. The most active metals in the galvanic corrosion chart, like aluminum, zinc, or. Web below is the galvanic corrosion chart, along with steps for using the chart properly to determine metal compatibility. Web below is a galvanic reaction chart for dissimilar metals. Electric current flows from plus to minus. Web the galvanic series chart below shows metals and their electrochemical voltage range (relative activity in flowing sea water). The below galvanic corrion chart or anodic index table shows anodic index for different materials. Web there are four elements necessary for corrosion to occur in a galvanic cell: A typical rule of thumb is that. Web below, we give a brief overview of galvanic corrosion and provide a galvanic corrosion chart to help fabricators and machinists avoid using the wrong metal. Web the metal with the higher potential forms the anode and is corroded. Web galvanic corrosion (some times called dissimilar metal corrosion) is the process by which the materials in contact with each other oxidizes or corrodes. Electric current flows from plus to minus. Web there are four elements necessary for corrosion to occur in a galvanic cell: The larger the separation distance in the electromotive chart between the two metals in contact, the. Web the galvanic corrosion table ranks metals from the most “active” to the least active. However, understanding how it works and the steps that can be taken to protect against. Galvanic corrosion (also called bimetallic corrosion or dissimilar metal corrosion) is an electrochemical process in which one metal corrodes preferentially when it is in electrical contact with another, in the presence of an electrolyte. This chart is designed to assist in broadly assessing the risk of galvanic corrosion associated with a given metal coming. Web by knowing the relationships of the metals in the series, galvanic compatibility can be determined, preventing the possible harmful effects of galvanic. The below galvanic corrion chart or anodic index table shows anodic index for different materials. Web galvanic corrosion (some times called dissimilar metal corrosion) is the process by which the materials in contact with each other oxidizes or corrodes. Web the galvanic corrosion table ranks metals from the most “active” to the least active. Web the metal with the higher. Web galvanic corrosion is of particular concern in design and material selection. However, understanding how it works and the steps that can be taken to protect against. Web the increased corrosion of the anode is called “galvanic corrosion.” galvanic corrosion is sometimes used to extend the life of materials (i.e. Web below is the galvanic corrosion chart, along with steps. Web typically, the presence of an electrolyte (eg. Web galvanic corrosion (some times called dissimilar metal corrosion) is the process by which the materials in contact with each other oxidizes or corrodes. For any combination of dissimilar metals, the metal with the lower number will act. Web the galvanic corrosion table ranks metals from the most “active” to the least. This phenomenon is named after italian ph… However, understanding how it works and the steps that can be taken to protect against. Web when corrosion does occur, the anodic material is the most likely to corrode, whereas the cathodic material is the least likely to corrode. Water) is necessary to promote galvanic corrosion. Web galvanic corrosion is of particular concern. Web the galvanic series chart below shows metals and their electrochemical voltage range (relative activity in flowing sea water). Water) is necessary to promote galvanic corrosion. For any combination of dissimilar metals, the metal with the lower number will act. The below galvanic corrion chart or anodic index table shows anodic index for different materials. Web when corrosion does occur,. We consider two metals compatible if their emf. The closer together the material are on the chart to the right, the less. However, understanding how it works and the steps that can be taken to protect against. Zinc coatings on carbon steel and. Web galvanic corrosion (some times called dissimilar metal corrosion) is the process by which the materials in. Web typically, the presence of an electrolyte (eg. The larger the separation distance in the electromotive chart between the two metals in contact, the. Web the galvanic series chart below shows metals and their electrochemical voltage range (relative activity in flowing sea water). Material selection is important because different metals come into contact with each other and. Web the increased. Web below is a galvanic reaction chart for dissimilar metals. Web to minimize galvanic corrosion, select fasteners based on their material compatibility with the substrates. Galvanic corrosion (also called bimetallic corrosion or dissimilar metal corrosion) is an electrochemical process in which one metal corrodes preferentially when it is in electrical contact with another, in the presence of an electrolyte. This. Web typically, the presence of an electrolyte (eg. Web galvanic corrosion (some times called dissimilar metal corrosion) is the process by which the materials in contact with each other oxidizes or corrodes. Web galvanic corrosion is of particular concern in design and material selection. A typical rule of thumb is that. Web to minimize galvanic corrosion, select fasteners based on. Material selection is important because different metals come into contact with each other and. However, understanding how it works and the steps that can be taken to protect against. This phenomenon is named after italian ph… Fastened of galvanic corrosion in joint, it’s. We consider two metals compatible if their emf. Web galvanic corrosion (some times called dissimilar metal corrosion) is the process by which the materials in contact with each other oxidizes or corrodes. Electric current flows from plus to minus. The closer together the material are on the chart to the right, the less. Web the galvanic series chart below shows metals and their electrochemical voltage range (relative activity in flowing sea water). Web below is a galvanic reaction chart for dissimilar metals. Fastened of galvanic corrosion in joint, it’s. This chart is designed to assist in broadly assessing the risk of galvanic corrosion associated with a given metal coming. For any combination of dissimilar metals, the metal with the lower number will act. Web the metal with the higher potential forms the anode and is corroded. A typical rule of thumb is that. Galvanic corrosion (also called bimetallic corrosion or dissimilar metal corrosion) is an electrochemical process in which one metal corrodes preferentially when it is in electrical contact with another, in the presence of an electrolyte. Water) is necessary to promote galvanic corrosion. The below galvanic corrion chart or anodic index table shows anodic index for different materials. Web the increased corrosion of the anode is called “galvanic corrosion.” galvanic corrosion is sometimes used to extend the life of materials (i.e. Web the galvanic corrosion table ranks metals from the most “active” to the least active. Zinc coatings on carbon steel and.Galvanic Corrosion CMP Products Limited
Galvanic Series (electrochemical series)
GALVANICCORROSIONTABLE CMP Products Limited
Galvanic Action Corrosion Prevention Architect's Blog
Galvanic Corrosion SSINA
Galvanic Corrosion [with Chart] EngineerExcel
Galvanic Corrosion Chart
Galvanic Corrosion Common Questions Answered
Galvanic Corrosion Chart PDF Corrosion Electrochemistry
Galvanic Corrosion Chart Metals
A Similar Galvanic Reaction Is Exploited In Primary Cells To Generate A Useful Electrical Voltage To Power Portable Devices.
Web There Are Four Elements Necessary For Corrosion To Occur In A Galvanic Cell:
Web When Corrosion Does Occur, The Anodic Material Is The Most Likely To Corrode, Whereas The Cathodic Material Is The Least Likely To Corrode.
We Consider Two Metals Compatible If Their Emf.
Related Post:

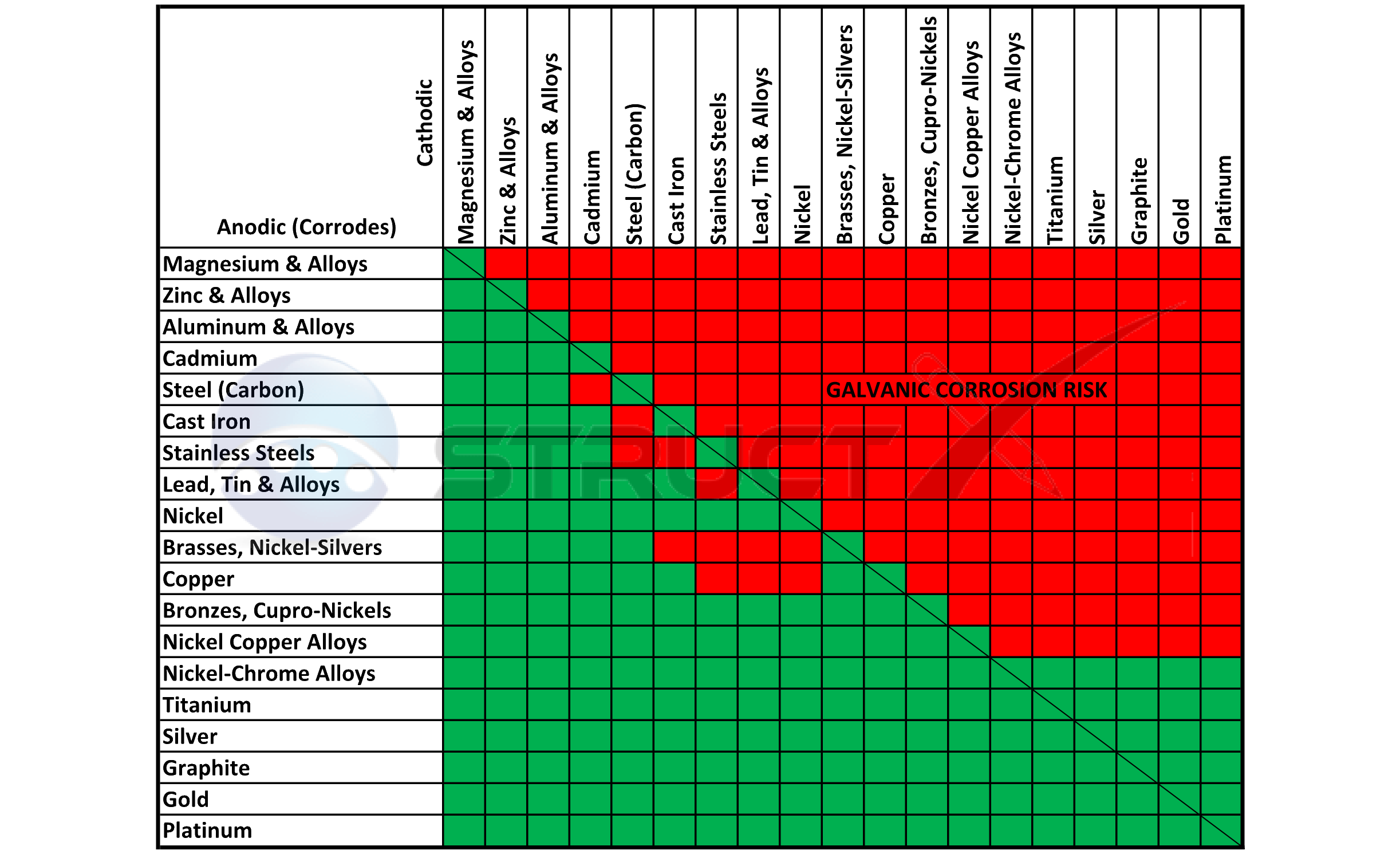



![Galvanic Corrosion [with Chart] EngineerExcel](https://engineerexcel.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/03/galvanic-corrosion-chart.png)