Diuretic Conversion Chart
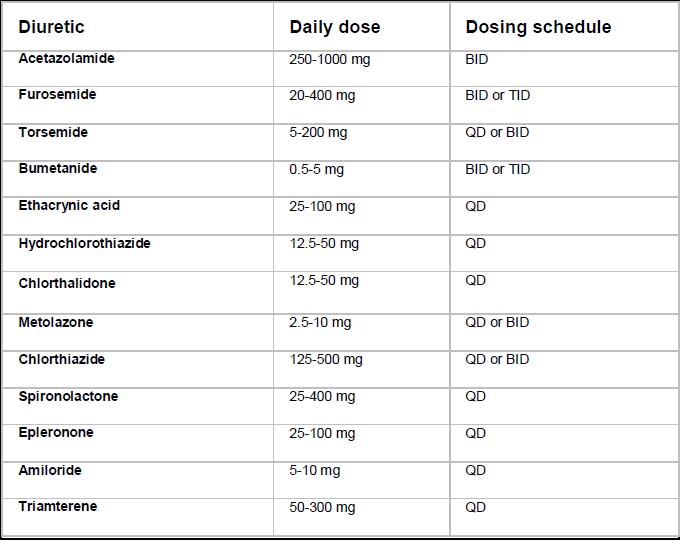
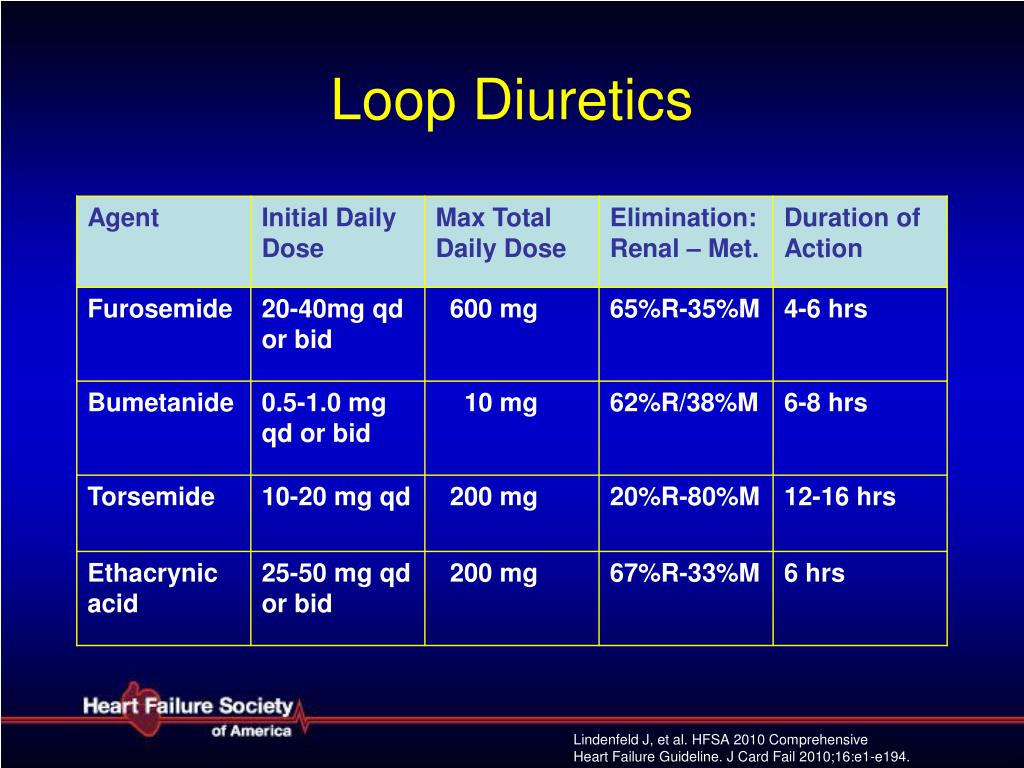
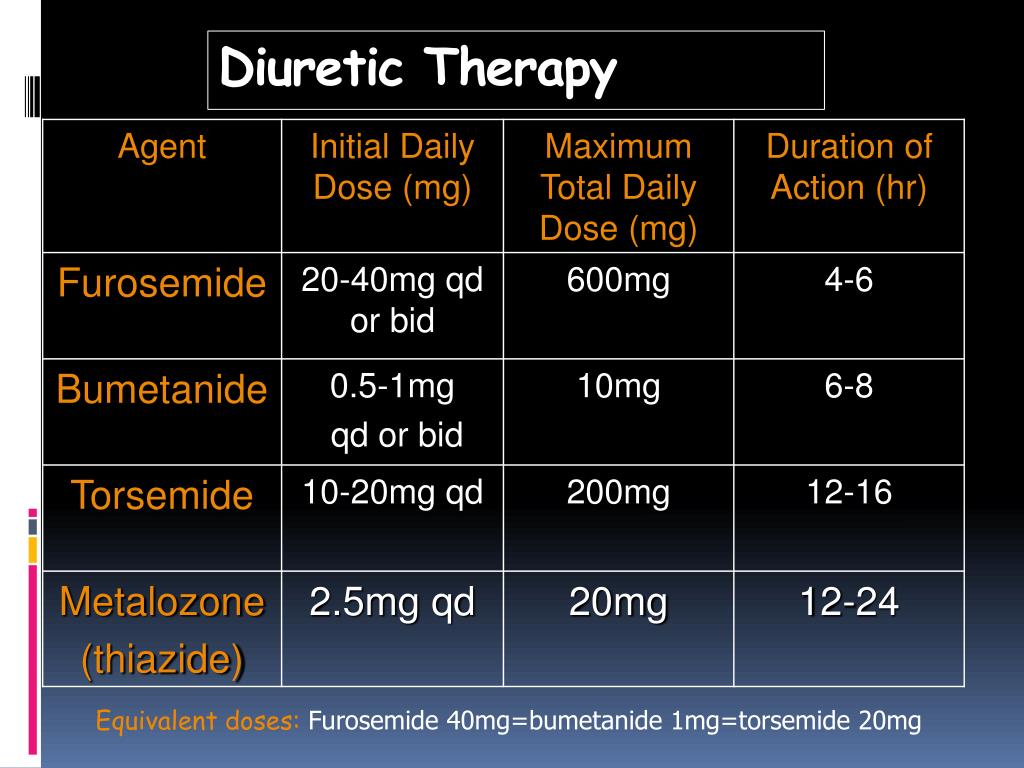
Diuretic Conversion Chart - Po:iv = oral to intravenous dosing conversion. Web the equivalent doses of bumetanide, furosemide, and torsemide are as follows: The most commonly used loop diuretics are furosemide, bumetanide, and torsemide, which are sulfonamide derivatives. Current iv dosing regimen during admission, renal function, previous home diuretic dose, and reason for decompensation. Furosemide has a roughly 1:2 conversion of iv:po, but oral bioavailability is variable so this is a very rough conversion. A metric of diuretic responsiveness with prognostic importance in acute decompensated heart failure. Web bumetanide has a 1:1 conversion of iv:po. Convert intravenous loop diuretic to oral diuretic dose. Albumin binding & tubular entry. Web this review will primarily focus on loop diuretic agents as the mainstays of diuretic therapy for hf, but will also discuss other adjuncts to loop diuretic therapy such as thiazides that are primarily used when there is diuretic resistance. Loop diuretics have high albumin binding (>90%), so they aren't freely filtered into the tubule. Web this review will primarily focus on loop diuretic agents as the mainstays of diuretic therapy for hf, but will also discuss other adjuncts to loop diuretic therapy such as thiazides that are primarily used when there is diuretic resistance. Po:iv = oral to intravenous dosing conversion. Web the equivalent doses of bumetanide, furosemide, and torsemide are as follows: The most commonly used loop diuretics are furosemide, bumetanide, and torsemide, which are sulfonamide derivatives. Web po = oral dosing. A metric of diuretic responsiveness with prognostic importance in acute decompensated heart failure. Torsemide (demadex) 20 x 2 thiazide diuretic daily dose (mg) metolazone dose conversion factor metolazone (zaroxolyn) 1 x 1 hydrochlorothiazide (hydrodiuril) 6 / 6. Web several factors should be taken into consideration when determining an appropriate oral diuretic dose to maintain euvolemia: Web the loop diuretics are highly protein bound and therefore enter the tubule primarily by secretion in the proximal tubule, rather than by glomerular filtration. Diuretic dose equivalency table loop diuretic daily dose (mg) furosemide dose conversion factor furosemide (lasix) 40 x 1. Torsemide (demadex) 20 x 2 thiazide diuretic daily dose (mg) metolazone dose conversion factor metolazone (zaroxolyn) 1 x 1 hydrochlorothiazide (hydrodiuril) 6 / 6. The most commonly used loop diuretics are furosemide, bumetanide, and torsemide, which are sulfonamide derivatives. This activity reviews. Current iv dosing regimen during admission, renal function, previous home diuretic dose, and reason for decompensation. Web po = oral dosing. Po:iv = oral to intravenous dosing conversion. Web the equivalent doses of bumetanide, furosemide, and torsemide are as follows: Web this review will primarily focus on loop diuretic agents as the mainstays of diuretic therapy for hf, but will. Convert intravenous loop diuretic to oral diuretic dose. Web po = oral dosing. Web the loop diuretics are highly protein bound and therefore enter the tubule primarily by secretion in the proximal tubule, rather than by glomerular filtration. Loop diuretics have high albumin binding (>90%), so they aren't freely filtered into the tubule. Furosemide has a roughly 1:2 conversion of. Web the equivalent doses of bumetanide, furosemide, and torsemide are as follows: Convert intravenous loop diuretic to oral diuretic dose. This activity reviews the indications, action, and contraindications for diuretics as a valuable agent in treating heart failure, hypertension, ascites, etc., (and other disorders when applicable). Torsemide (demadex) 20 x 2 thiazide diuretic daily dose (mg) metolazone dose conversion factor. Furosemide has a roughly 1:2 conversion of iv:po, but oral bioavailability is variable so this is a very rough conversion. Web the equivalent doses of bumetanide, furosemide, and torsemide are as follows: Diuretic dose equivalency table loop diuretic daily dose (mg) furosemide dose conversion factor furosemide (lasix) 40 x 1. Web the loop diuretics are highly protein bound and therefore. Web the loop diuretics are highly protein bound and therefore enter the tubule primarily by secretion in the proximal tubule, rather than by glomerular filtration. This activity reviews the indications, action, and contraindications for diuretics as a valuable agent in treating heart failure, hypertension, ascites, etc., (and other disorders when applicable). Loop diuretics have high albumin binding (>90%), so they. Loop diuretics have high albumin binding (>90%), so they aren't freely filtered into the tubule. Web this review will primarily focus on loop diuretic agents as the mainstays of diuretic therapy for hf, but will also discuss other adjuncts to loop diuretic therapy such as thiazides that are primarily used when there is diuretic resistance. Furosemide has a roughly 1:2. Convert intravenous loop diuretic to oral diuretic dose. Current iv dosing regimen during admission, renal function, previous home diuretic dose, and reason for decompensation. Web the equivalent doses of bumetanide, furosemide, and torsemide are as follows: Web diuretics are a class of drugs. Web the loop diuretics are highly protein bound and therefore enter the tubule primarily by secretion in. Web the equivalent doses of bumetanide, furosemide, and torsemide are as follows: Web the loop diuretics are highly protein bound and therefore enter the tubule primarily by secretion in the proximal tubule, rather than by glomerular filtration. Loop diuretics have high albumin binding (>90%), so they aren't freely filtered into the tubule. Web several factors should be taken into consideration. Web bumetanide has a 1:1 conversion of iv:po. Web the equivalent doses of bumetanide, furosemide, and torsemide are as follows: Web diuretics are a class of drugs. Diuretic dose equivalency table loop diuretic daily dose (mg) furosemide dose conversion factor furosemide (lasix) 40 x 1. Web po = oral dosing. Albumin binding & tubular entry. Web the equivalent doses of bumetanide, furosemide, and torsemide are as follows: Web several factors should be taken into consideration when determining an appropriate oral diuretic dose to maintain euvolemia: Convert intravenous loop diuretic to oral diuretic dose. Torsemide (demadex) 20 x 2 thiazide diuretic daily dose (mg) metolazone dose conversion factor metolazone (zaroxolyn) 1 x 1 hydrochlorothiazide (hydrodiuril) 6 / 6. Web po = oral dosing. The most commonly used loop diuretics are furosemide, bumetanide, and torsemide, which are sulfonamide derivatives. Web the loop diuretics are highly protein bound and therefore enter the tubule primarily by secretion in the proximal tubule, rather than by glomerular filtration. Loop diuretics have high albumin binding (>90%), so they aren't freely filtered into the tubule. A metric of diuretic responsiveness with prognostic importance in acute decompensated heart failure. Furosemide has a roughly 1:2 conversion of iv:po, but oral bioavailability is variable so this is a very rough conversion. Current iv dosing regimen during admission, renal function, previous home diuretic dose, and reason for decompensation. Web bumetanide has a 1:1 conversion of iv:po. This activity reviews the indications, action, and contraindications for diuretics as a valuable agent in treating heart failure, hypertension, ascites, etc., (and other disorders when applicable).Diuretics summary table Thiazides and Related Diuretics GrepMed
Diseases of Volume Regulation Diuretic Therapy Renal and Urology News
PPT HFSA 2010 Comprehensive Heart Failure Practice Guideline
Loop Diuretic Equivalence Conversions. 7,8 Download Scientific Diagram
Diuretic Dose Conversion Chart
13 Best Images of Medical Assistant Printable Worksheets Medical
Loop diuretic conversion Equivalent Doses Furosemide GrepMed
Diuretics Abdominal Key
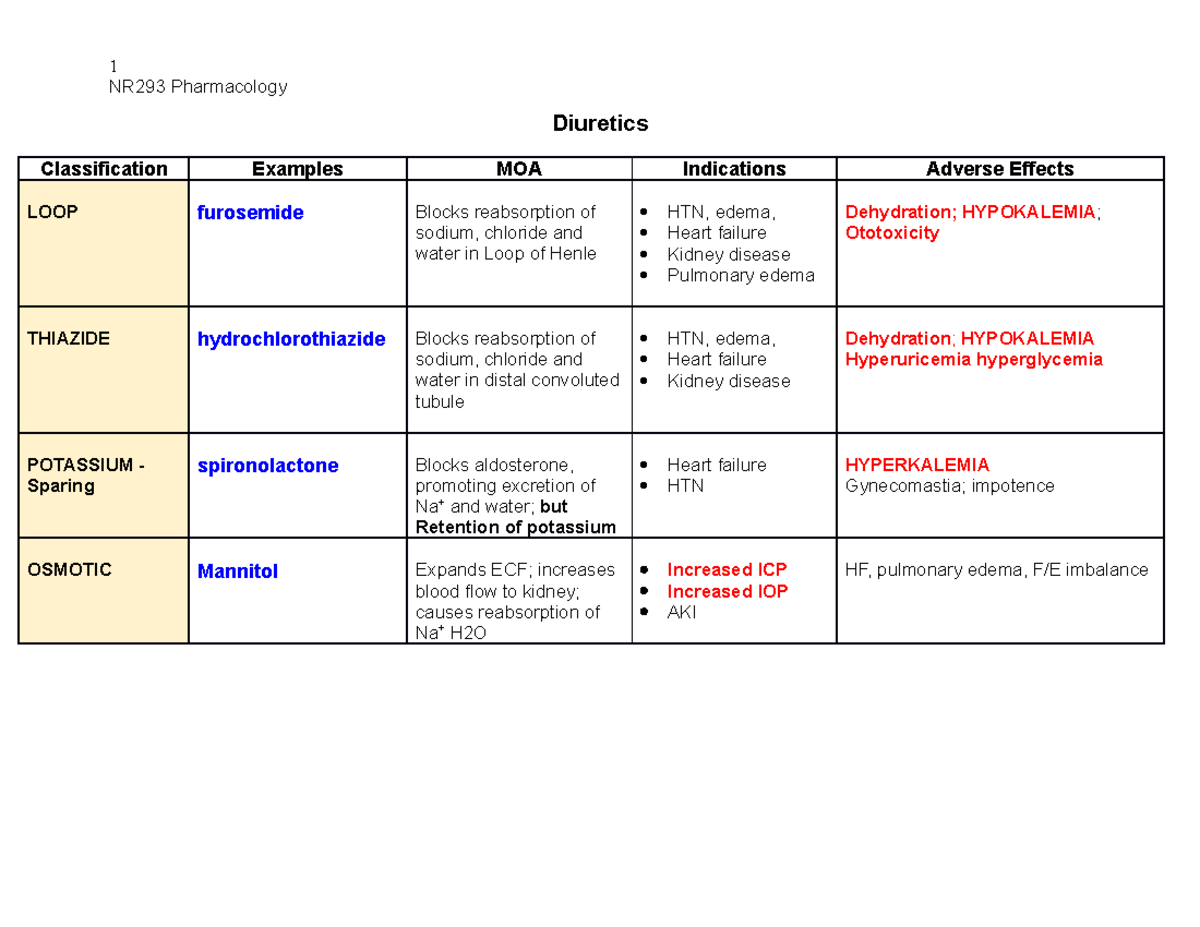
Diuretics Chart medications to help memorize medications 1 NR293
Diuretics Cheat Sheet Pharmacology, Drug cards, Nursing pharmacology
Web Diuretics Are A Class Of Drugs.
Web This Review Will Primarily Focus On Loop Diuretic Agents As The Mainstays Of Diuretic Therapy For Hf, But Will Also Discuss Other Adjuncts To Loop Diuretic Therapy Such As Thiazides That Are Primarily Used When There Is Diuretic Resistance.
Diuretic Dose Equivalency Table Loop Diuretic Daily Dose (Mg) Furosemide Dose Conversion Factor Furosemide (Lasix) 40 X 1.
Po:iv = Oral To Intravenous Dosing Conversion.
Related Post: