Chart Of Macromolecules
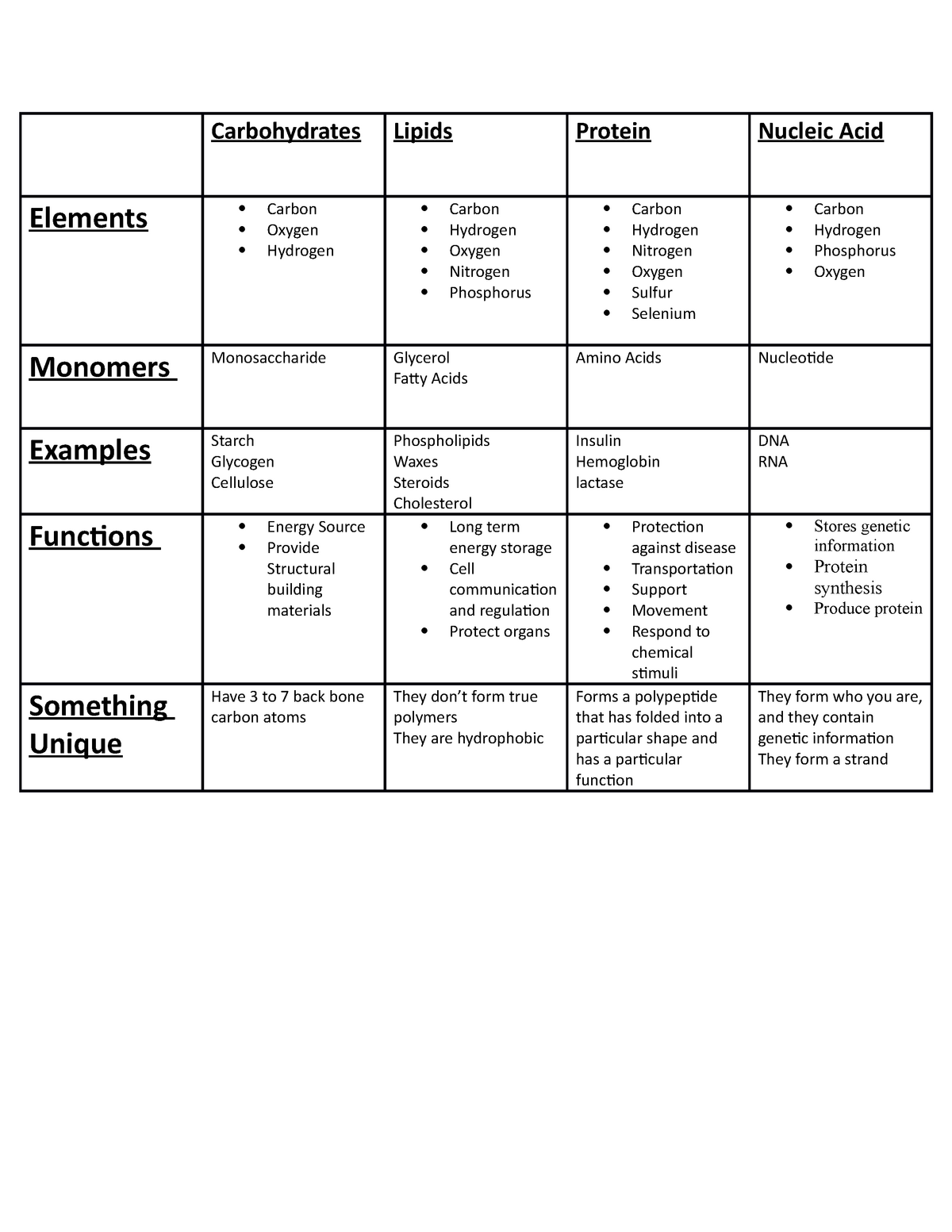
Chart Of Macromolecules - Web macromolecule proteins monomer name and chemical composition and name of bond between adjacent monomers amino acids peptide bonds types of this macromolecule. Unit 4 elements of life. Unit 2 water, acids, and bases. Organic compound composed of carbon, hydrogen, oxygen ratio of 1:2:1 monomer is monosaccharide (ch2o)n, where n is any whole number from 3 to 8,. Web the four groups of macromolecules, shown in the table below, are essential to the structure and function of a ce. Carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids. There are four major classes of biological macromolecules. Web biological macromolecules are important cellular components and perform a wide array of functions necessary for the survival and growth of living organisms. Unit 5 energy and enzymes. These large macromolecules may consist of. These large macromolecules may consist of. Proteins, carbohydrates, nucleic acids, and lipids are the four major classes of biological. They can have very different shapes, although the most. Unit 5 energy and enzymes. Web all living things are made up of four main classes of macromolecules: Web carbohydrates are biological molecules made of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen in a ratio of roughly one carbon atom (c ) to one water molecule (h 2 o ). Unit 4 elements of life. Web in biology, macromolecules refer to large organic molecules that form by polymerization, a process that joins smaller units called monomers via covalent bonds. The house select committee investigating january 6 has asked rep. Web macromolecule proteins monomer name and chemical composition and name of bond between adjacent monomers amino acids peptide bonds types of this macromolecule. Proteins, carbohydrates, nucleic acids, and lipids are the four major classes of biological macromolecules—large. (b) carbon dioxide escapes from the solution when the cap is. Unit 6 structure of a cell. The house select committee investigating january 6 has asked rep. Jim jordan, one of former president donald trump`s top congressional allies, to. There are four major classes of biological macromolecules. Web the four groups of macromolecules, shown in the table below, are essential to the structure and function of a ce. Proteins, carbohydrates, nucleic acids, and lipids are the four major classes of biological. Web properties, structure, and function of biological macromolecules. Different types of biological macromolecules. The house select committee investigating january 6 has asked rep. This activity will have students identifying the monomer, polymer, function, elements, and examples for the following four macromolecules (1). Web a macromolecule is a very large molecule important to biological processes, such as a protein or nucleic acid. Web unit 1 intro to biology. Web macromolecule proteins monomer name and. Web distinguish between the four classes of macromolecules carbohydrates are a group of macromolecules that are a vital energy source for the cell, provide. (b) carbon dioxide escapes from the solution when the cap is. Principles of biology ii (biol 2108) university. The house select committee investigating january 6 has asked rep. Web in the avengers activity students will test. Web in biology, macromolecules refer to large organic molecules that form by polymerization, a process that joins smaller units called monomers via covalent bonds. Their molecular weights can range from the thousands to the millions. Web biological macromolecules are large molecules, necessary for life, that are built from smaller organic molecules. They can have very different shapes, although the most.. It is composed of thousands of covalently bonded atoms. The image below depicts how the bacterial protein barnase undergoes. Web lew lab’s innovative microscopy charts amyloid beta’s underlying structure, could yield insight into neurodegenerative disease. The large molecules of all living things fall into just four main classes. Web unit 1 intro to biology. Web the four groups of macromolecules, shown in the table below, are essential to the structure and function of a ce. Web biological macromolecules are large molecules, necessary for life, that are built from smaller organic molecules. Web biological macromolecules are important cellular components and perform a wide array of functions necessary for the survival and growth of living organisms.. (a) the boiling point of seawater is higher than that of pure water. These large macromolecules may consist of. Web macromolecule proteins monomer name and chemical composition and name of bond between adjacent monomers amino acids peptide bonds types of this macromolecule. The house select committee investigating january 6 has asked rep. Unit 4 elements of life. Unit 6 structure of a cell. Web a macromolecule is a very large molecule important to biological processes, such as a protein or nucleic acid. Their molecular weights can range from the thousands to the millions. Web macromolecules are very large molecules. Carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids. Web in the avengers activity students will test evidence against a positive and negative control for four types of macromolecules to determine which ingredient was. Their molecular weights can range from the thousands to the millions. Circle the three classes that are called macromolecules. Principles of biology ii (biol 2108) university. (a) the boiling point of seawater is higher than. Unit 2 water, acids, and bases. Web carbohydrates are biological molecules made of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen in a ratio of roughly one carbon atom (c ) to one water molecule (h 2 o ). The large molecules of all living things fall into just four main classes. Web there are four classes of macromolecules that constitute all living matter: Web explain each of the following statements: Web proteins, carbohydrates, nucleic acids, and lipids are the four major classes of biological macromolecules—large molecules necessary for life that are built. Web all living things are made up of four main classes of macromolecules: Organic compound composed of carbon, hydrogen, oxygen ratio of 1:2:1 monomer is monosaccharide (ch2o)n, where n is any whole number from 3 to 8,. Their molecular weights can range from the thousands to the millions. The house select committee investigating january 6 has asked rep. Unit 4 elements of life. Web lew lab’s innovative microscopy charts amyloid beta’s underlying structure, could yield insight into neurodegenerative disease. Web distinguish between the four classes of macromolecules carbohydrates are a group of macromolecules that are a vital energy source for the cell, provide. It is composed of thousands of covalently bonded atoms. (b) carbon dioxide escapes from the solution when the cap is. Unit 5 energy and enzymes.Macromolecules Chart Rae Rocks Teaching
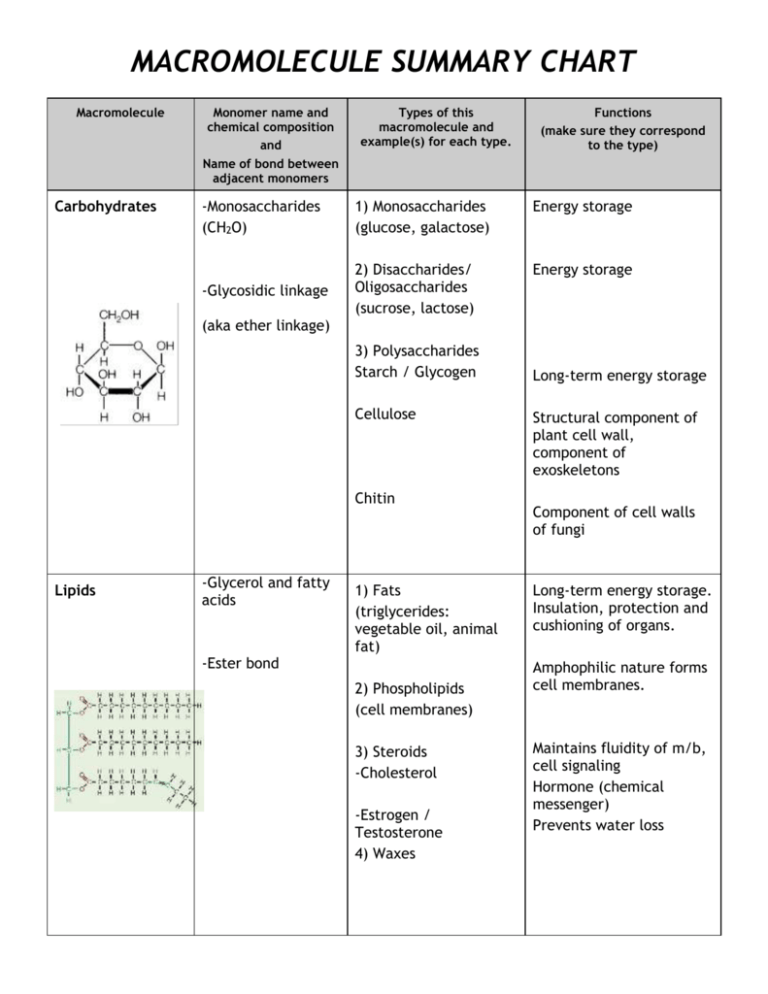
macromolecule summary chart
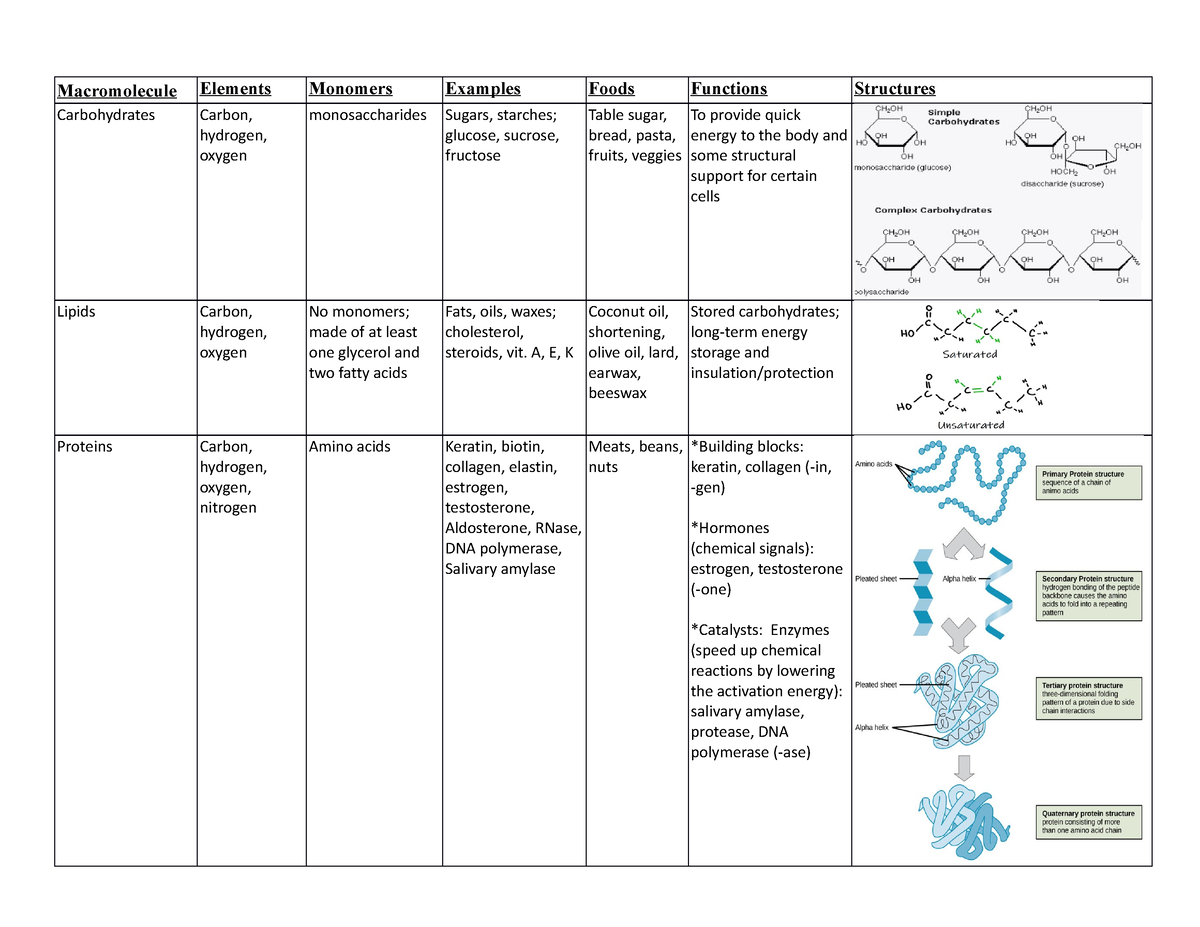
Macromolecules Table Macromolecule Elements Monomers Examples Foods
Biochemistry Macromolecules Chart A Visual Reference of Charts Chart
Macromolecules chart Lecture notes A Carbohydrates Elements Carbon
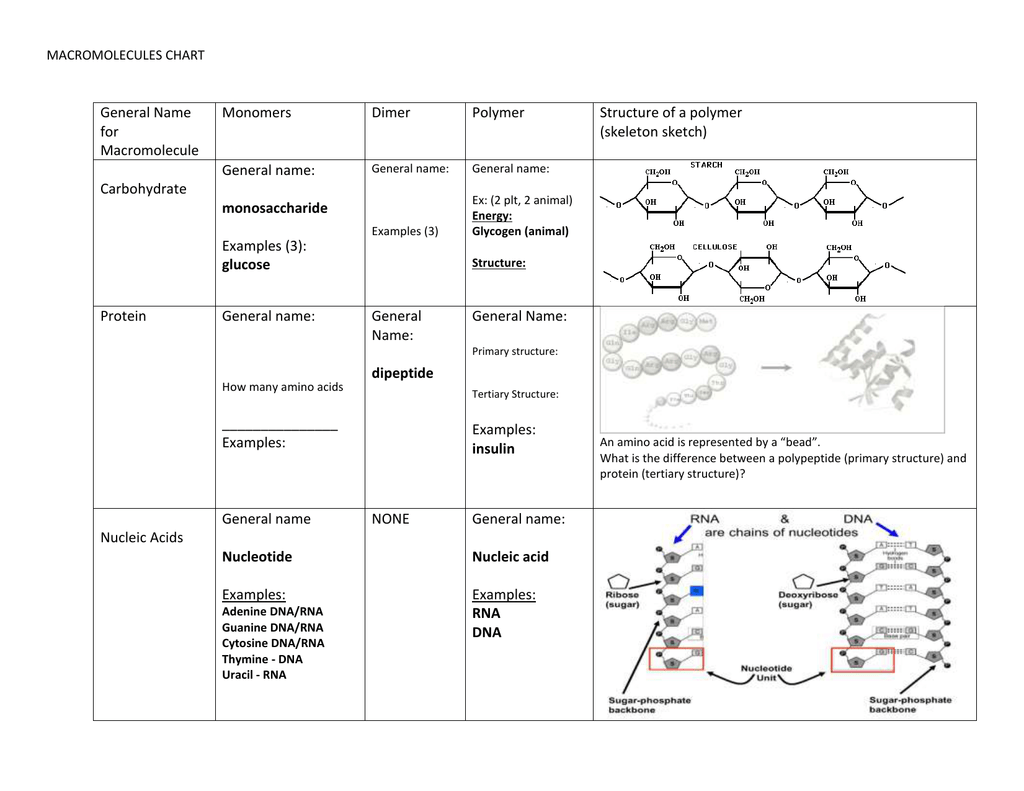
MACROMOLECULES CHART General Name for Macromolecule
2.3 Biologically Important Macromolecules Biology LibreTexts
Macromolecules Chart Structures
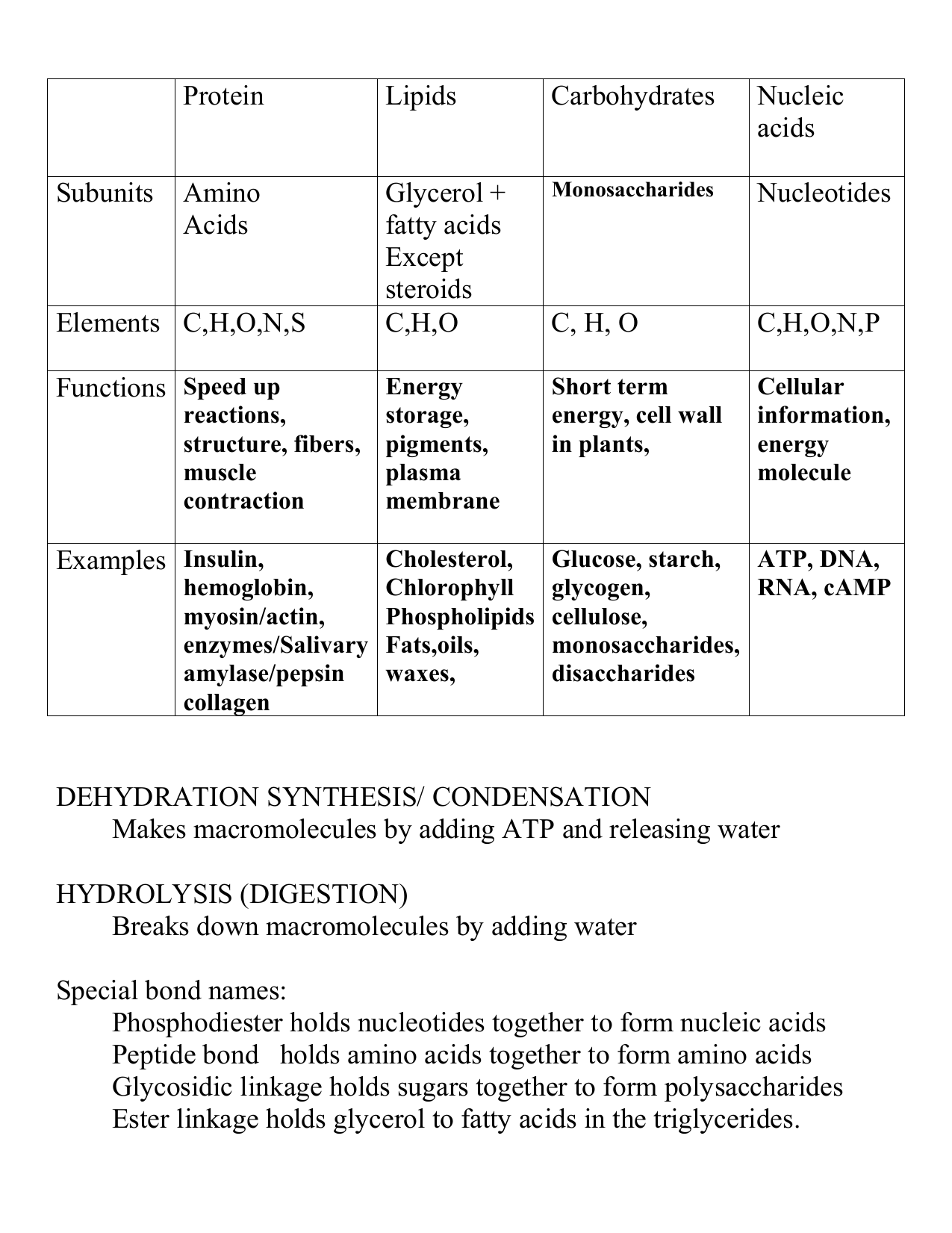
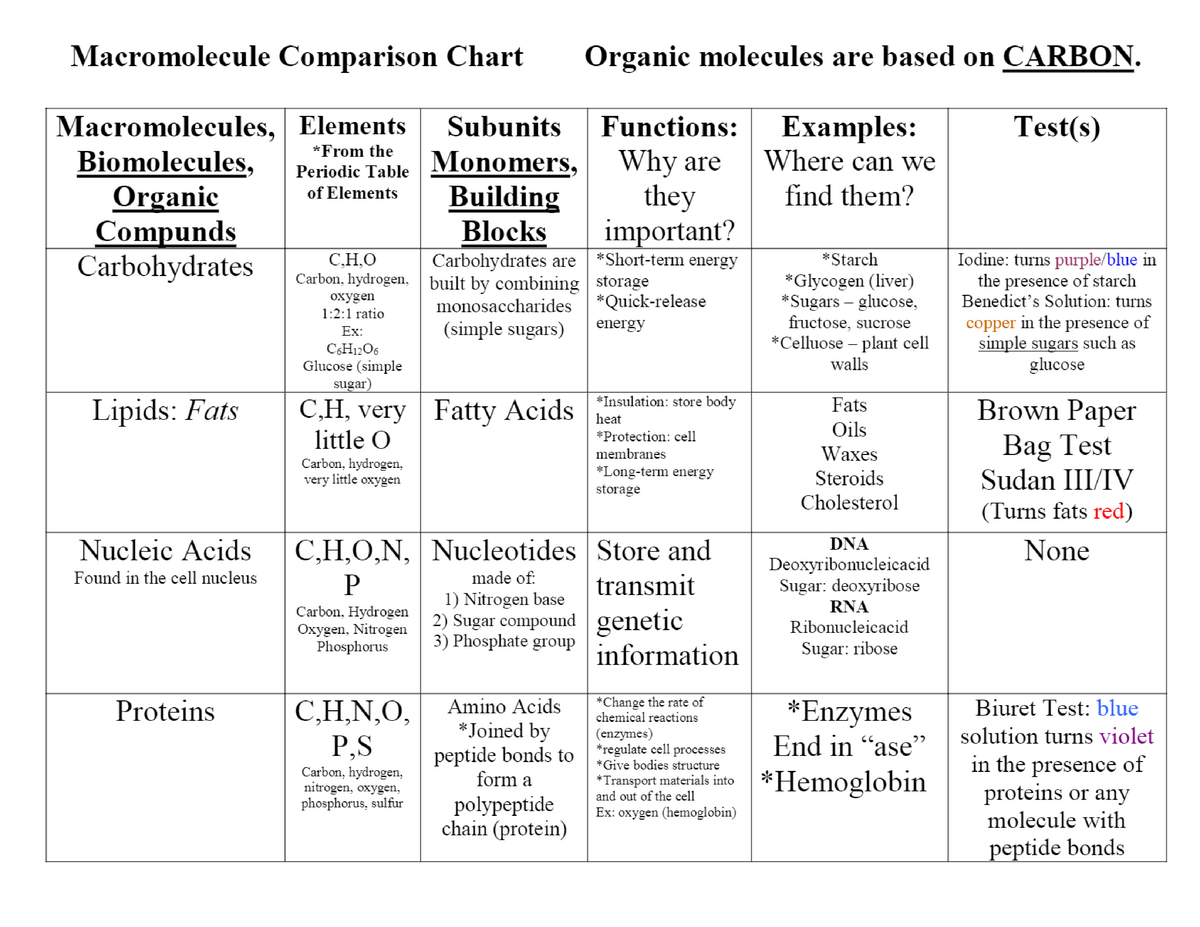
Macromolecule Comparison Chart Organic Bio201 Studocu
Pre IB/GT Biology 1 Macromolecules Chart Diagram Quizlet
Web Unit 1 Intro To Biology.
Web Cuelure, An Effective Lure Specifically Targeting Tephritid Fruit Flies, Has Been Widely Adopted And Applied In The Monitoring And Control Of These Pests, Providing.
While They Have Different Structures And Functions,.
Perimeter College At Georgia State University.
Related Post: