Brain Waves Chart
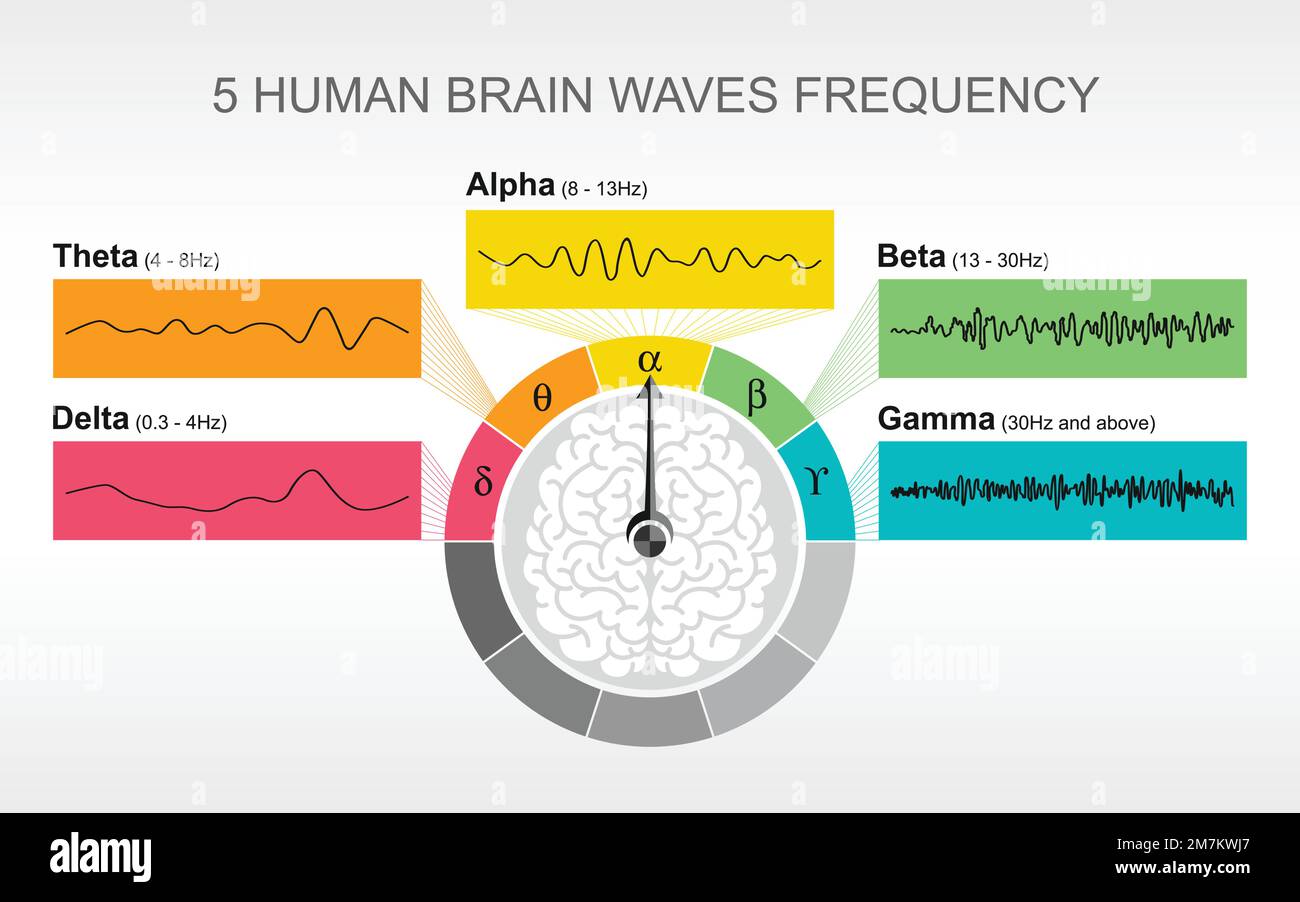
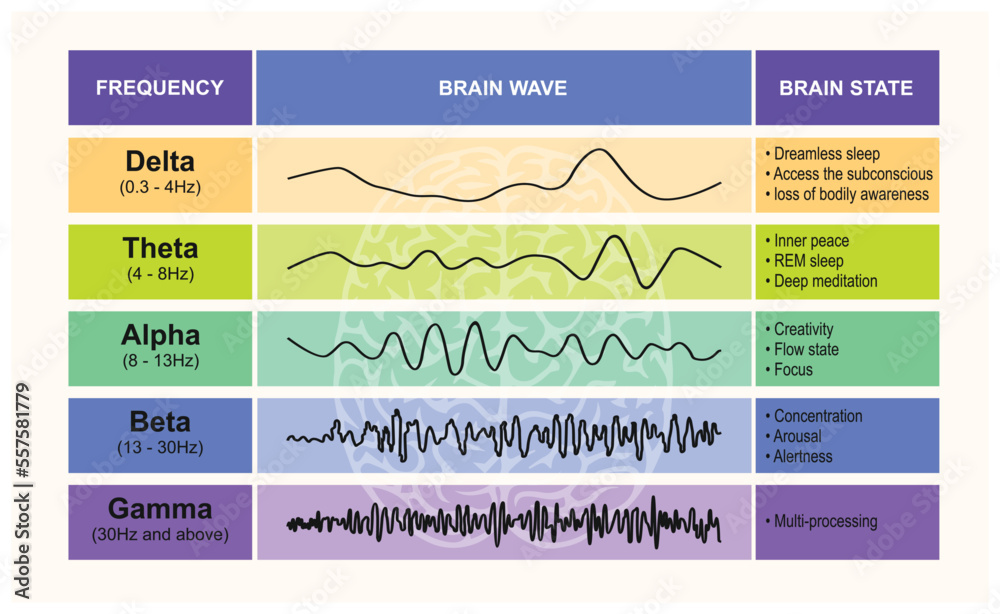
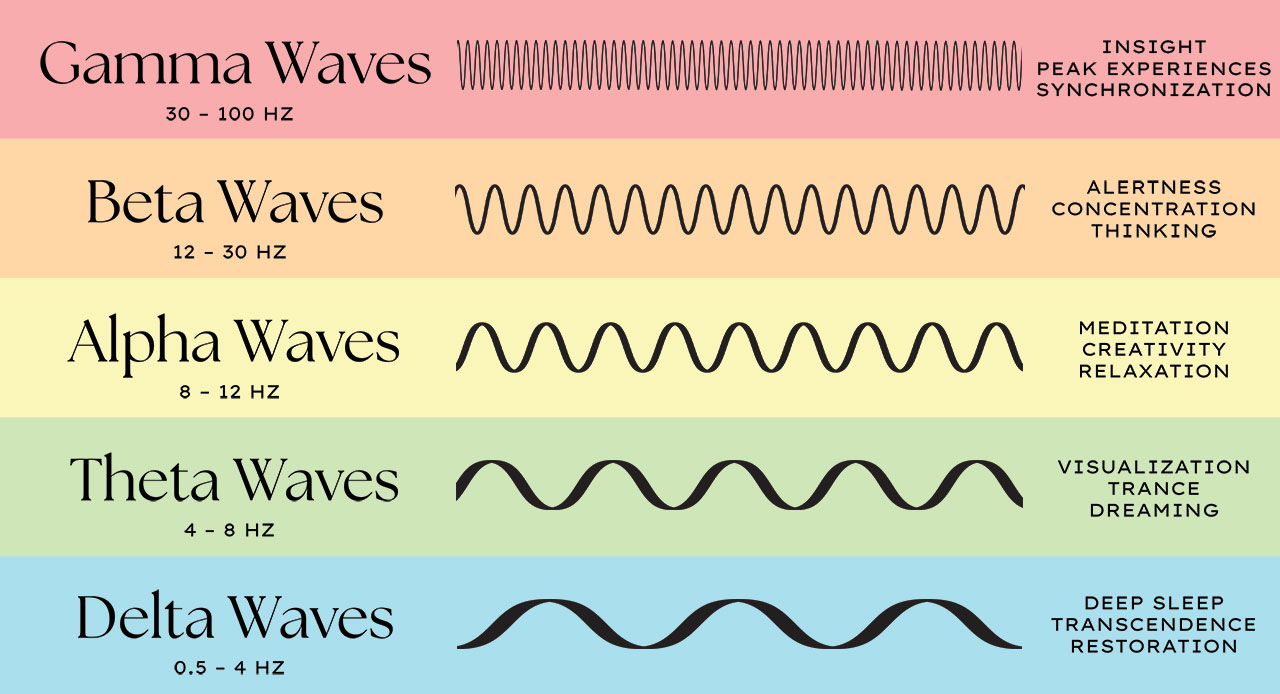
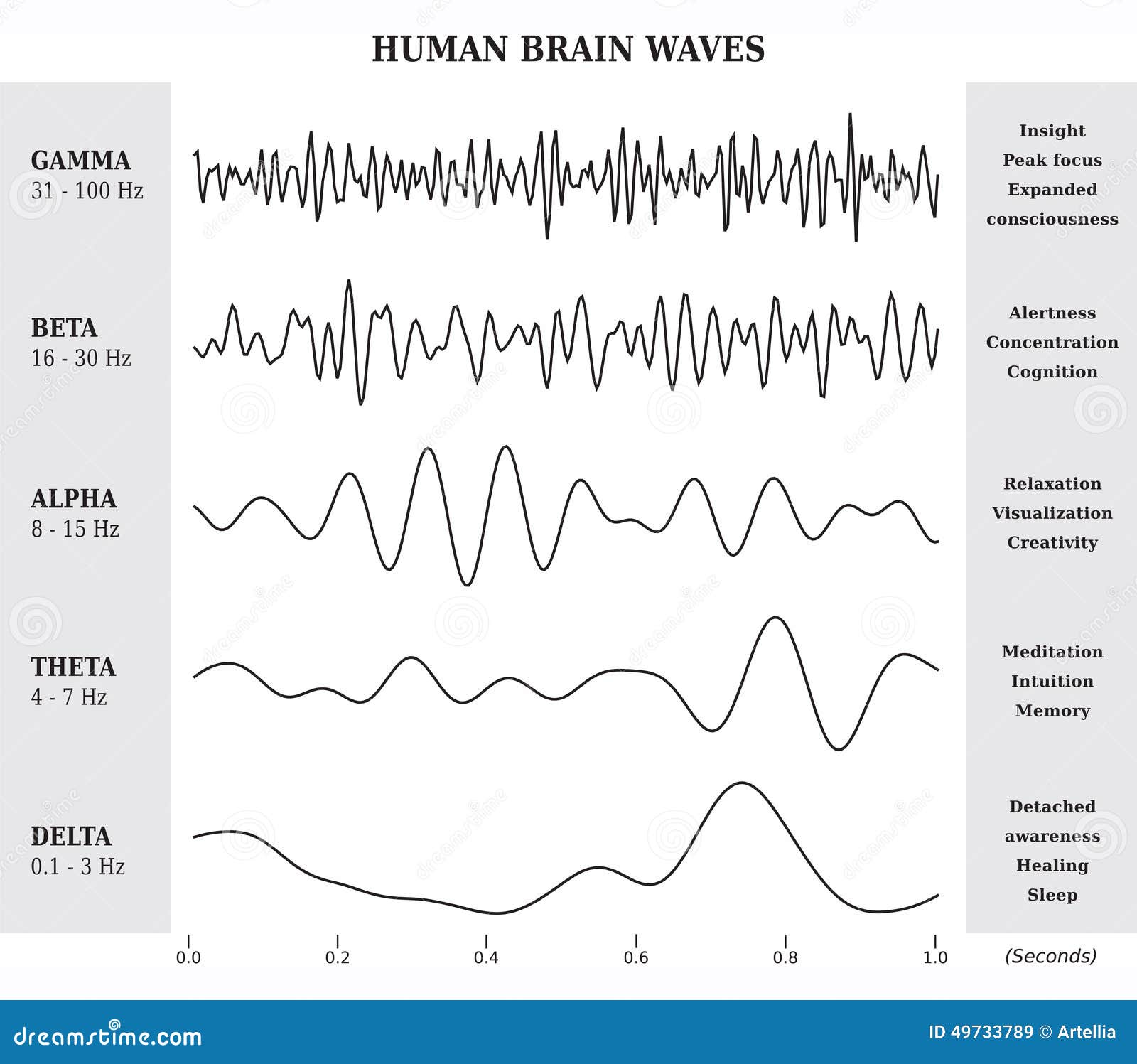
Brain Waves Chart - Web these smooth, oscillating sine wave frequencies enhance your mind’s ability to relax into a quiet and peaceful meditative state. They are measured in cycles per second, or hertz (hz). Web theta brain waves are slower than gamma, beta, and alpha waves, but faster than delta waves. Low, the deep beat of a drum. The five brain waves in order of highest frequency to lowest are as follows: Your brain produces theta waves when you’re drifting off to sleep or just before you wake up. However, this is actually referring to brain waves which specifically come from measuring brain activity using. Alpha, beta, delta, and theta. With practice and experience it is possible to reach the theta state through meditation, but you can speed up this process with mind amend's brain entrainment programs. Gamma, beta, alpha, theta, and delta. By amplifying the brainwave synchronization effects, deep carrier frequencies allow you to achieve a far deeper level of meditation, quickly, safely and easily. Each brainwave has a distinct purpose and helps us behave, think, move and process. Web brain waves are electrical impulses that flow through the brain, creating patterns of activity. Alpha, beta, delta, and theta. Gamma, beta, alpha, theta, delta. Web these smooth, oscillating sine wave frequencies enhance your mind’s ability to relax into a quiet and peaceful meditative state. Web brain state work can be couched in terms such as alpha, delta and so forth. Fast activity refers to a higher frequency and often smaller amplitude. Web theta brain waves are slower than gamma, beta, and alpha waves, but faster than delta waves. The five brain waves in order of highest frequency to lowest are as follows: They are measured in cycles per second, or hertz (hz). Gamma, beta, alpha, theta, and delta. Fast activity refers to a higher frequency and often smaller amplitude. Web the six anatomical layers of the mammalian brain cortex show distinct patterns of electrical activity which are consistent throughout the entire cortex and across several animal species, including humans, an mit study. However, this is actually referring to brain waves which specifically come from measuring brain activity using. Low, the deep beat of a drum. Each brainwave has a distinct purpose and helps us behave, think, move and process. Web the six anatomical layers of the mammalian brain cortex show distinct patterns of electrical activity which are consistent throughout the entire cortex. By amplifying the brainwave synchronization effects, deep carrier frequencies allow you to achieve a far deeper level of meditation, quickly, safely and easily. Fast activity refers to a higher frequency and often smaller amplitude. Gamma, beta, alpha, theta, delta. Gamma, beta, alpha, theta, and delta. Web brain state work can be couched in terms such as alpha, delta and so. Web brain state work can be couched in terms such as alpha, delta and so forth. Each brainwave has a distinct purpose and helps us behave, think, move and process. Web brain waves are electrical impulses that flow through the brain, creating patterns of activity. There are four main types of brain waves: Web these smooth, oscillating sine wave frequencies. Web these smooth, oscillating sine wave frequencies enhance your mind’s ability to relax into a quiet and peaceful meditative state. Gamma, beta, alpha, theta, and delta. Alpha, beta, delta, and theta. Web when the brain is alert and performing complex computations, the cerebral cortex, the wrinkled outer surface of the brain, thrums with cortical band oscillations in the gamma wavelength;. Web when the brain is alert and performing complex computations, the cerebral cortex, the wrinkled outer surface of the brain, thrums with cortical band oscillations in the gamma wavelength; The five brain waves in order of highest frequency to lowest are as follows: Web theta brain waves are slower than gamma, beta, and alpha waves, but faster than delta waves.. Web brain waves are electrical impulses that flow through the brain, creating patterns of activity. Your brain produces theta waves when you’re drifting off to sleep or just before you wake up. Low, the deep beat of a drum. In some neurological disorders like schizophrenia, these waves are out of tune and the rhythm is out of sync. Web brain. Alpha, beta, delta, and theta. Web brain waves are electrical impulses that flow through the brain, creating patterns of activity. Low, the deep beat of a drum. Gamma, beta, alpha, theta, delta. With practice and experience it is possible to reach the theta state through meditation, but you can speed up this process with mind amend's brain entrainment programs. With practice and experience it is possible to reach the theta state through meditation, but you can speed up this process with mind amend's brain entrainment programs. Web theta brain waves are slower than gamma, beta, and alpha waves, but faster than delta waves. Web brain state work can be couched in terms such as alpha, delta and so forth.. Gamma, beta, alpha, theta, and delta. Web in all of us, you’ll find the following 5 brainwaves: By amplifying the brainwave synchronization effects, deep carrier frequencies allow you to achieve a far deeper level of meditation, quickly, safely and easily. Low, the deep beat of a drum. Web brain waves are electrical impulses that flow through the brain, creating patterns. Gamma, beta, alpha, theta, and delta. By amplifying the brainwave synchronization effects, deep carrier frequencies allow you to achieve a far deeper level of meditation, quickly, safely and easily. They are measured in cycles per second, or hertz (hz). Fast activity refers to a higher frequency and often smaller amplitude. With practice and experience it is possible to reach the theta state through meditation, but you can speed up this process with mind amend's brain entrainment programs. The five brain waves in order of highest frequency to lowest are as follows: Each brainwave has a distinct purpose and helps us behave, think, move and process. Web these smooth, oscillating sine wave frequencies enhance your mind’s ability to relax into a quiet and peaceful meditative state. Web when the brain is alert and performing complex computations, the cerebral cortex, the wrinkled outer surface of the brain, thrums with cortical band oscillations in the gamma wavelength; Gamma, beta, alpha, theta, delta. In some neurological disorders like schizophrenia, these waves are out of tune and the rhythm is out of sync. There are four main types of brain waves: However, this is actually referring to brain waves which specifically come from measuring brain activity using. Low, the deep beat of a drum. Web in all of us, you’ll find the following 5 brainwaves: Web the six anatomical layers of the mammalian brain cortex show distinct patterns of electrical activity which are consistent throughout the entire cortex and across several animal species, including humans, an mit study has found.Brainwave Frequencies Explained
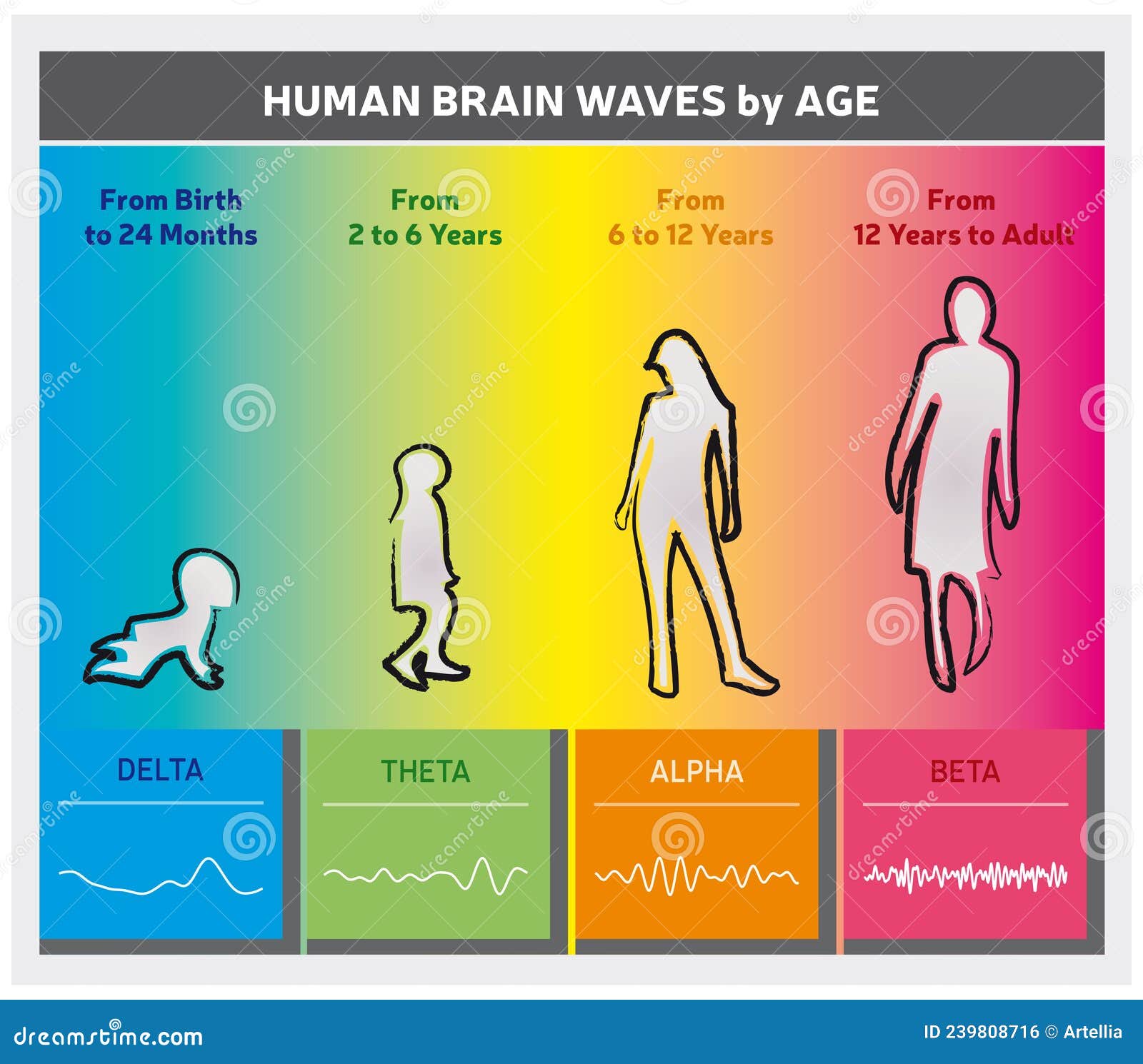
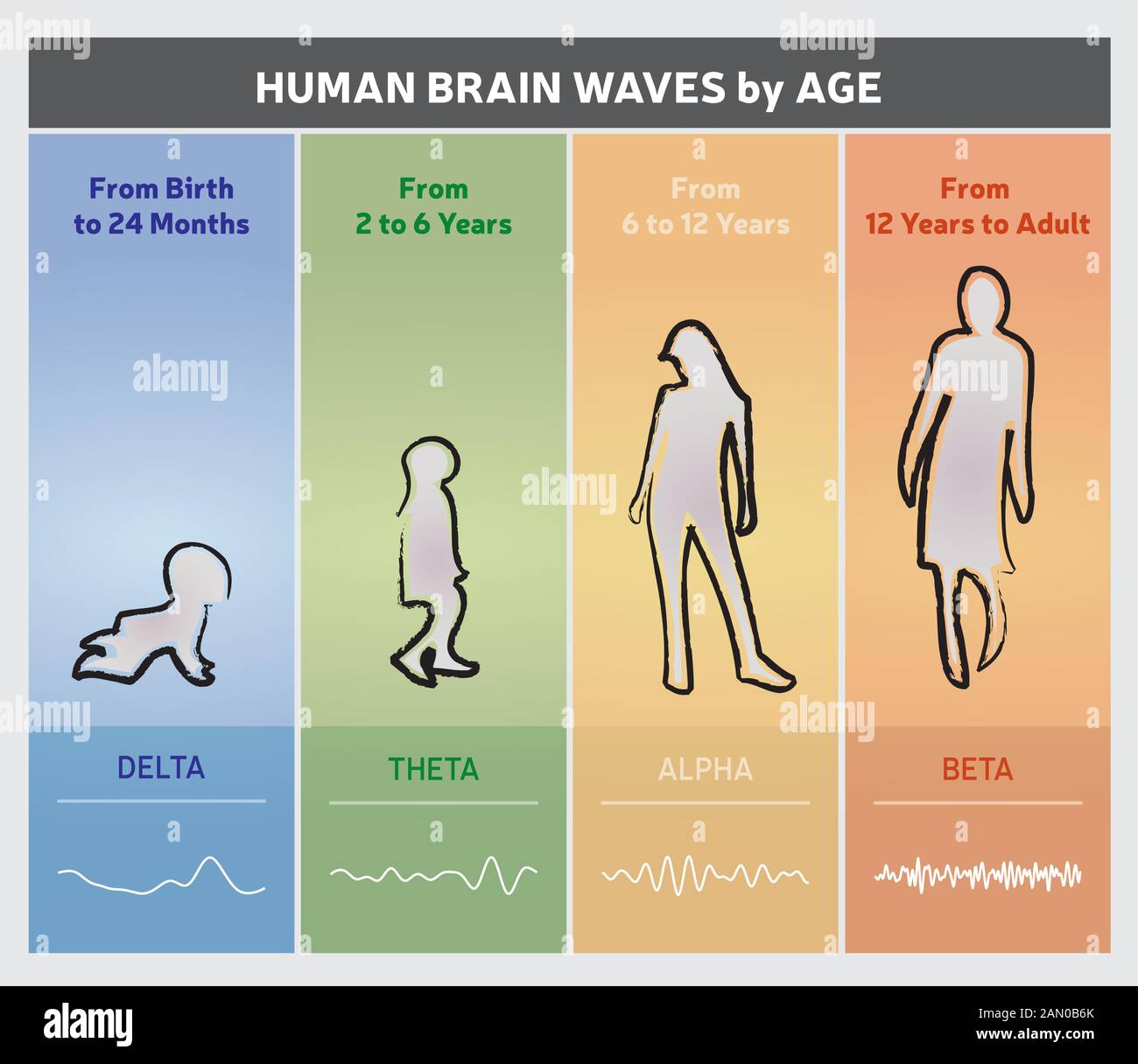
Human Brain Waves by Age Chart Diagram People Silhouettes Rainbow
Brain Waves Frequency Chart
Brain waves oscillating electric voltage Delta, Theta, Alpha, Beta
Brain waves Delta, Theta, Alpha, Beta, Gamma vector illustration chart
Understanding Brain Waves Beta, Alpha, Theta, Delta + Gamma
1,727 Brain wave chart Images, Stock Photos & Vectors Shutterstock
Human Brain Waves by Age Chart Diagram People Silhouettes English
Human Brain Waves Diagram / Chart / Illustration Stock Vector
Set of brain waves oscillation. Beta, alpha, theta, delta, gamma brain
Alpha, Beta, Delta, And Theta.
Your Brain Produces Theta Waves When You’re Drifting Off To Sleep Or Just Before You Wake Up.
Web Brain State Work Can Be Couched In Terms Such As Alpha, Delta And So Forth.
Web Brain Waves Are Electrical Impulses That Flow Through The Brain, Creating Patterns Of Activity.
Related Post: