Brain Frequency Chart
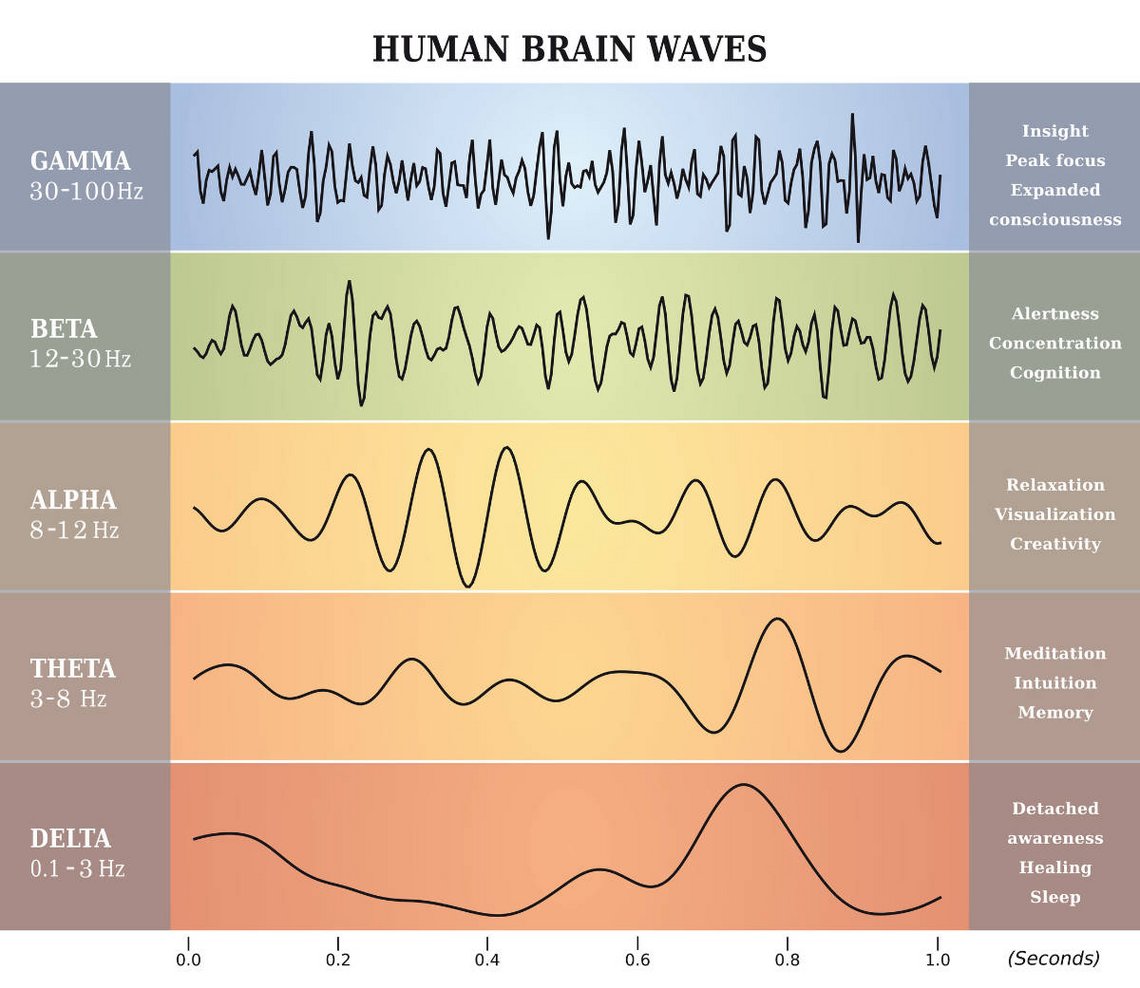
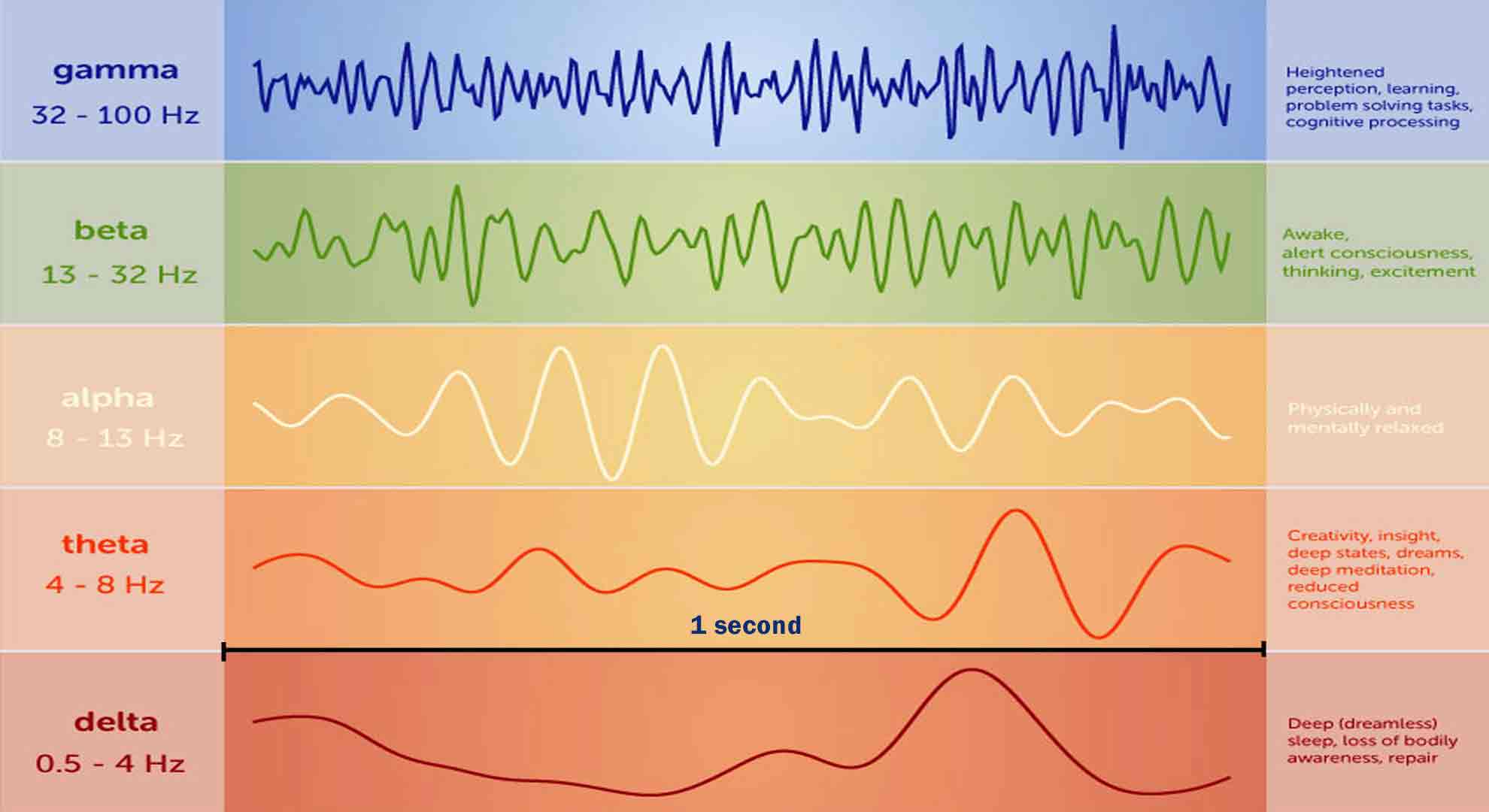
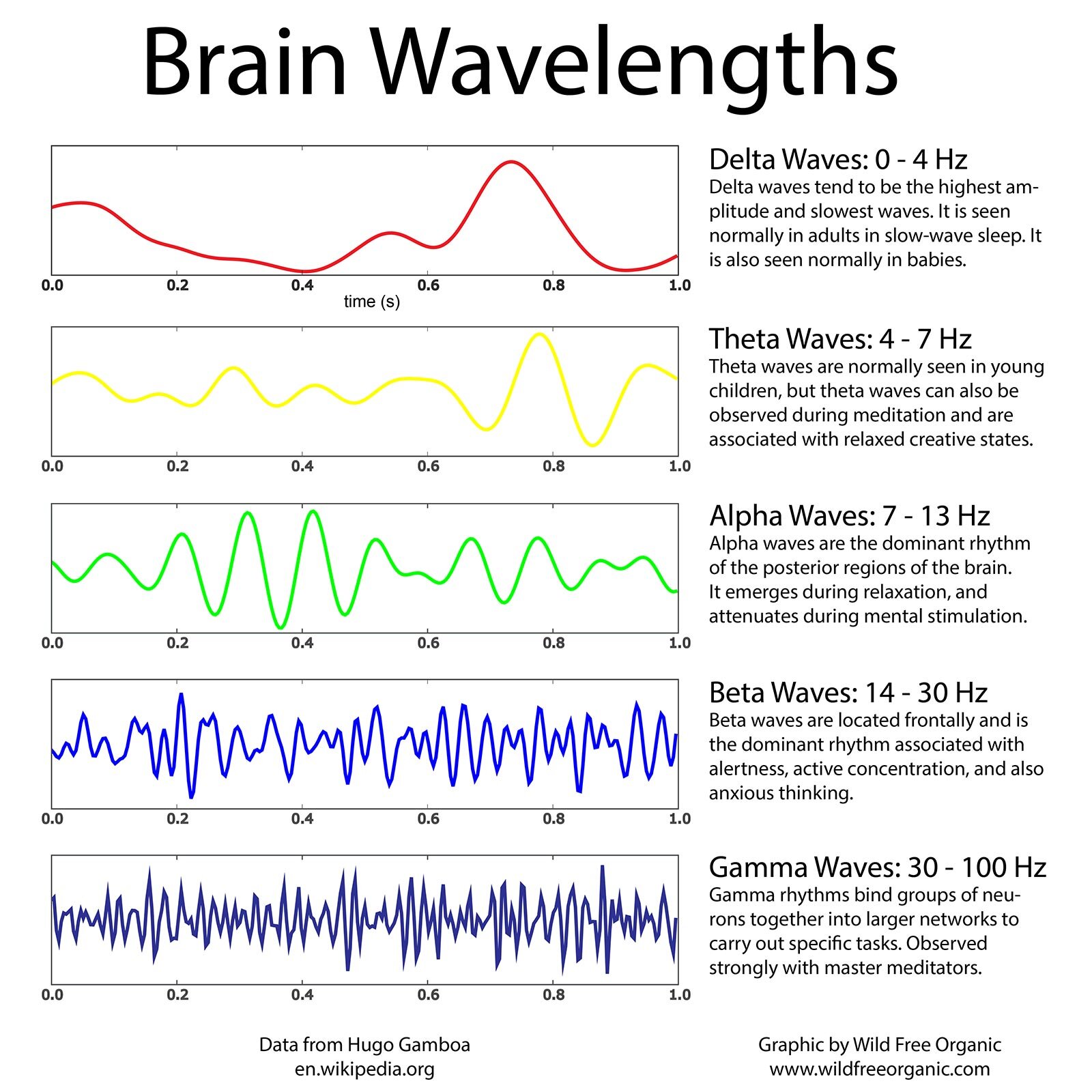
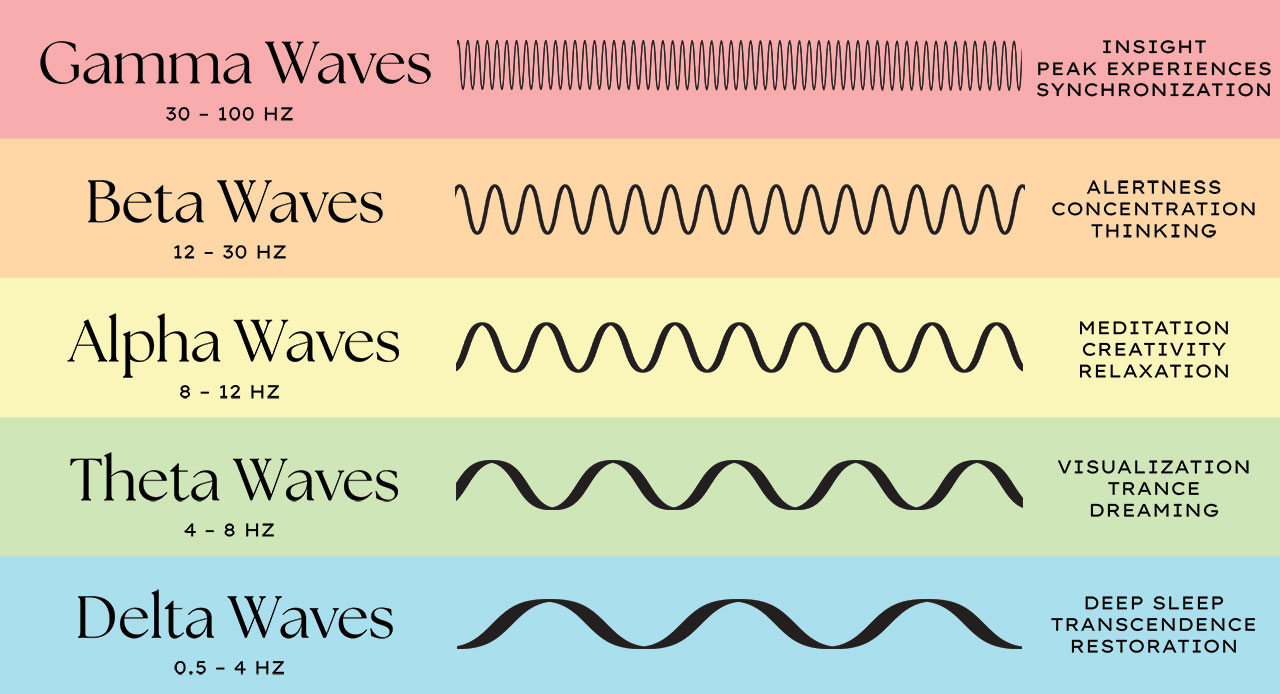
Brain Frequency Chart - Beta brain waves are involved in logical thinking, conscious thought and concentration. Electrodes are placed on specific sites on the scalp to detect and record the electrical impulses within the brain. Web theta brain waves are slower than gamma, beta, and alpha waves, but faster than delta waves. Alpha brain waves are most present when we are awake and relaxed. Your brain produces theta waves when you’re drifting off to sleep or just before you wake up. A frequency is the number of times a wave repeats itself within a second. These waves occur during strong mental activities such as studying and solving problems. Decreased awareness of the physical world. This brainwave frequency chart explains gamma, beta, alpha, theta, and delta waves. There are five different types of brainwaves. Web explore the different brainwave frequencies of consciousness. Web by measuring thousands of neurons along the surface, or cortex, of the brain in animals as they reacted to predictable and surprising images, the researchers observed that low frequency alpha and beta brain waves, or rhythms, originating in the brain’s frontal cognitive regions tamped down neural activity associated with predictable. Here’s a look at our different brain waves and what scientific studies have taught us about their features and characteristics: Web there are four main types of brain waves: Web brain waves are measured by frequency, which is cycles per second, or hertz (hz), and they range from very slow to very fast. Each type of brain wave is associated with a different state of consciousness. They are often compared to musical notes since each type of brain wave has its own “sound,” which is distinct from others. Your brain produces theta waves when you’re drifting off to sleep or just before you wake up. Beta waves, for example, are associated with wakefulness and alertness, while delta waves are associated with deep sleep. Web according to a recent definition, brain states are “recurring activity patterns distributed across the brain that emerge from physiological or cognitive processes”. Web brain waves are measured by frequency, which is cycles per second, or hertz (hz), and they range from very slow to very fast. By amplifying the brainwave synchronization effects, deep carrier frequencies allow you to achieve a far deeper level of meditation, quickly, safely and easily. Web theta brain waves are slower than gamma, beta, and alpha waves, but. Web the dominant frequency they communicate with each other determines our brainwave state. Your brain produces theta waves when you’re drifting off to sleep or just before you wake up. Decreased awareness of the physical world. Here’s a look at our different brain waves and what scientific studies have taught us about their features and characteristics: By amplifying the brainwave. The five brain waves in order of highest frequency to lowest are as follows: Web the dominant frequency they communicate with each other determines our brainwave state. Web there are five main types of brainwaves that occur at various stages of brain activity. Web explore the different brainwave frequencies of consciousness. Alpha waves, which measure between 8 and 12 hz,. Web like musical sounds, different states of mind are defined by distinct, characteristic waveforms, recognizable frequencies and rhythms in the electrical field of the brain. Web there are four main types of brain waves: Web these smooth, oscillating sine wave frequencies enhance your mind’s ability to relax into a quiet and peaceful meditative state. Discover innovative tools like the muse. Web at a glance, here are some of the benefits and functions associated with key brainwave frequencies. Gamma brain waves are the highest frequency band, and the range is by far the widest. Web the five types of brain waves and their associated frequencies are: Web in order of lowest frequency to higher, the five brain waves are: Web through. Gamma 40+ hz is experienced during extreme alertness, high energy and times of. While sleeping or meditating, the amount of beta waves decreases. Dominant brainwave in infants under one year old. Web the chart below shows the brainwave eeg (electroencephalography) graphs of the four major levels of brainwaves, their respective brainwave frequencies and their corresponding states of mind. Delta waves,. Web in order of lowest frequency to higher, the five brain waves are: Dominant brainwave in infants under one year old. They can be increased through meditation and mindfulness. Web according to a recent definition, brain states are “recurring activity patterns distributed across the brain that emerge from physiological or cognitive processes”. Web there are five main types of brainwaves. Web the eeg (electroencephalograph) measures brain waves of different frequencies within the brain. Web according to a recent definition, brain states are “recurring activity patterns distributed across the brain that emerge from physiological or cognitive processes”. Web there are 5 types of brain waves — alpha, beta, gamma, delta and theta. Web in order of lowest frequency to higher, the. Gamma brain waves are the highest frequency band, and the range is by far the widest. Web by measuring thousands of neurons along the surface, or cortex, of the brain in animals as they reacted to predictable and surprising images, the researchers observed that low frequency alpha and beta brain waves, or rhythms, originating in the brain’s frontal cognitive regions. Gamma brain waves are the highest frequency band, and the range is by far the widest. Web according to a recent definition, brain states are “recurring activity patterns distributed across the brain that emerge from physiological or cognitive processes”. The five brain waves in order of highest frequency to lowest are as follows: Web there are five main types of. They are often compared to musical notes since each type of brain wave has its own “sound,” which is distinct from others. Each type of brain wave is associated with a different state of consciousness. Your brain produces theta waves when you’re drifting off to sleep or just before you wake up. Theta waves, which are between 4 and 8 hz, occur during light sleep or deep relaxation. Web there are 5 types of brain waves — alpha, beta, gamma, delta and theta. Getting to know the 5 frequencies. Decreased awareness of the physical world. They can be increased through meditation and mindfulness. This brainwave frequency chart explains gamma, beta, alpha, theta, and delta waves. Discover innovative tools like the muse 2 headband and the muse s headband that revolutionize brain training for enhanced focus. Web the dominant frequency they communicate with each other determines our brainwave state. The five brain waves in order of highest frequency to lowest are as follows: Web explore the different brainwave frequencies of consciousness. Gamma brain waves are the highest frequency band, and the range is by far the widest. Web by measuring thousands of neurons along the surface, or cortex, of the brain in animals as they reacted to predictable and surprising images, the researchers observed that low frequency alpha and beta brain waves, or rhythms, originating in the brain’s frontal cognitive regions tamped down neural activity associated with predictable. A frequency is the number of times a wave repeats itself within a second.Set of brain waves oscillation. Beta, alpha, theta, delta, gamma brain
Brainwaves How your brain works
Brain Waves Chart
Human Brain Waves Diagram in Rainbow Colors with Explanations Alpha
Brain Waves Frequency Chart
Brain Waves Frequency Chart
Brain Waves Frequency Chart
Brainwave Frequencies Explained
Understanding Brain Waves Beta, Alpha, Theta, Delta + Gamma
Brainwave Frequencies Explained
Web The Five Types Of Brain Waves And Their Associated Frequencies Are:
Delta, Theta, Alpha, Beta And Gamma.
Electrodes Are Placed On Specific Sites On The Scalp To Detect And Record The Electrical Impulses Within The Brain.
Beta Waves, For Example, Are Associated With Wakefulness And Alertness, While Delta Waves Are Associated With Deep Sleep.
Related Post: