6 Kingdoms Chart
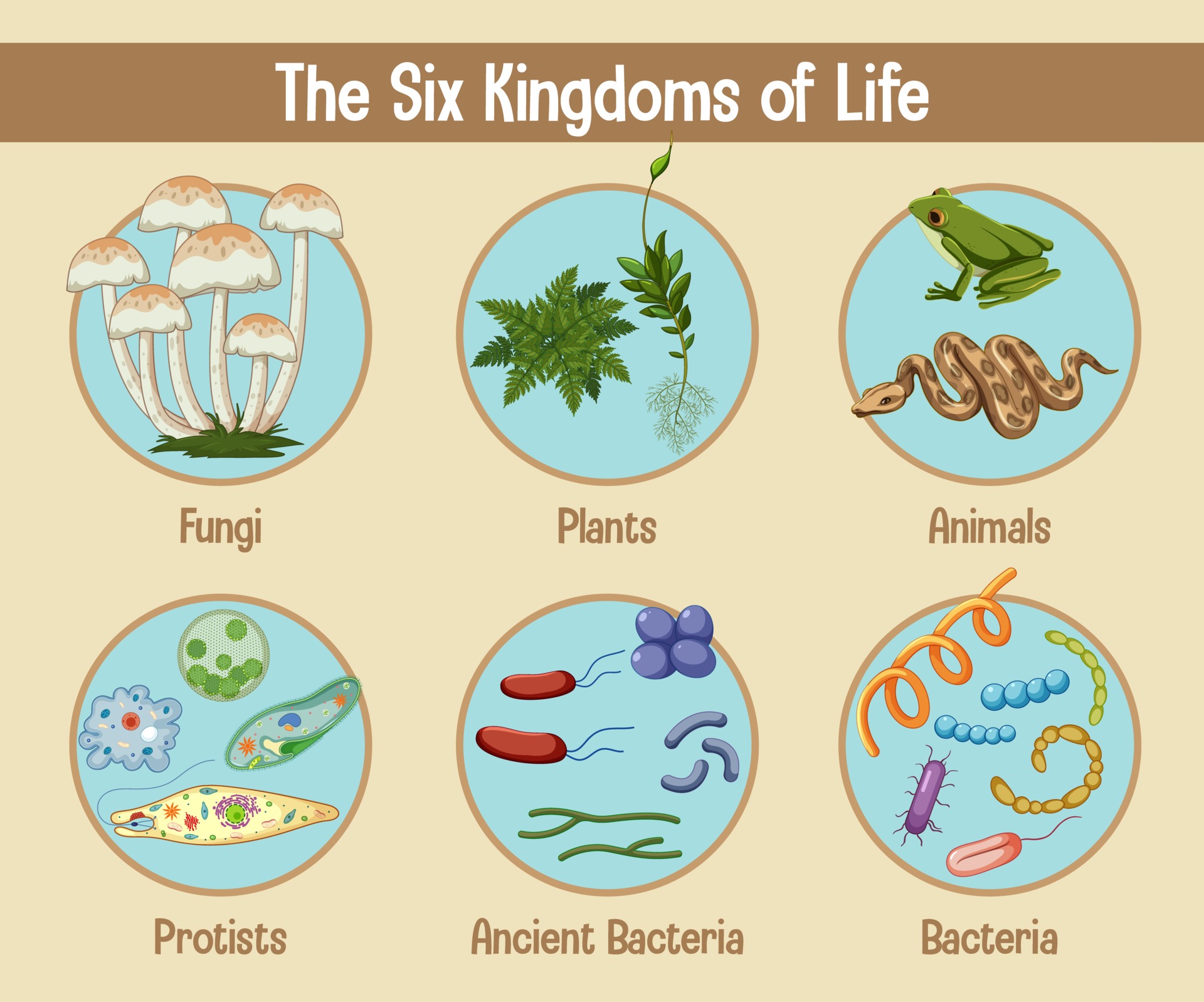
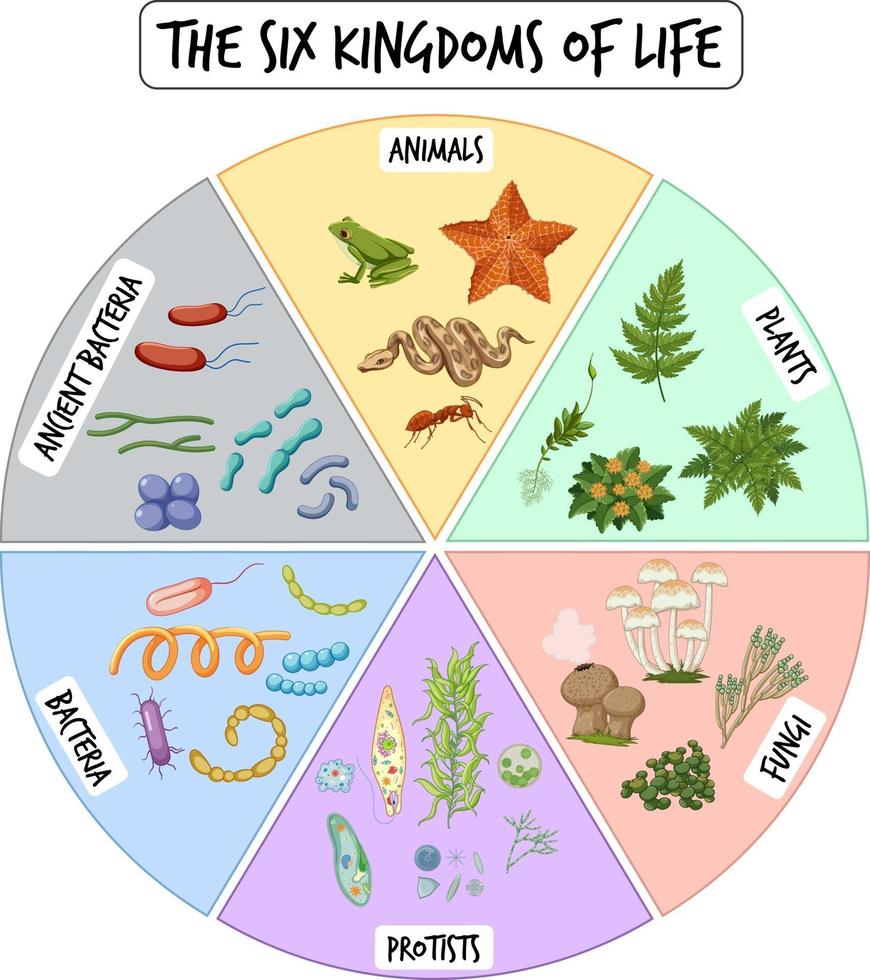
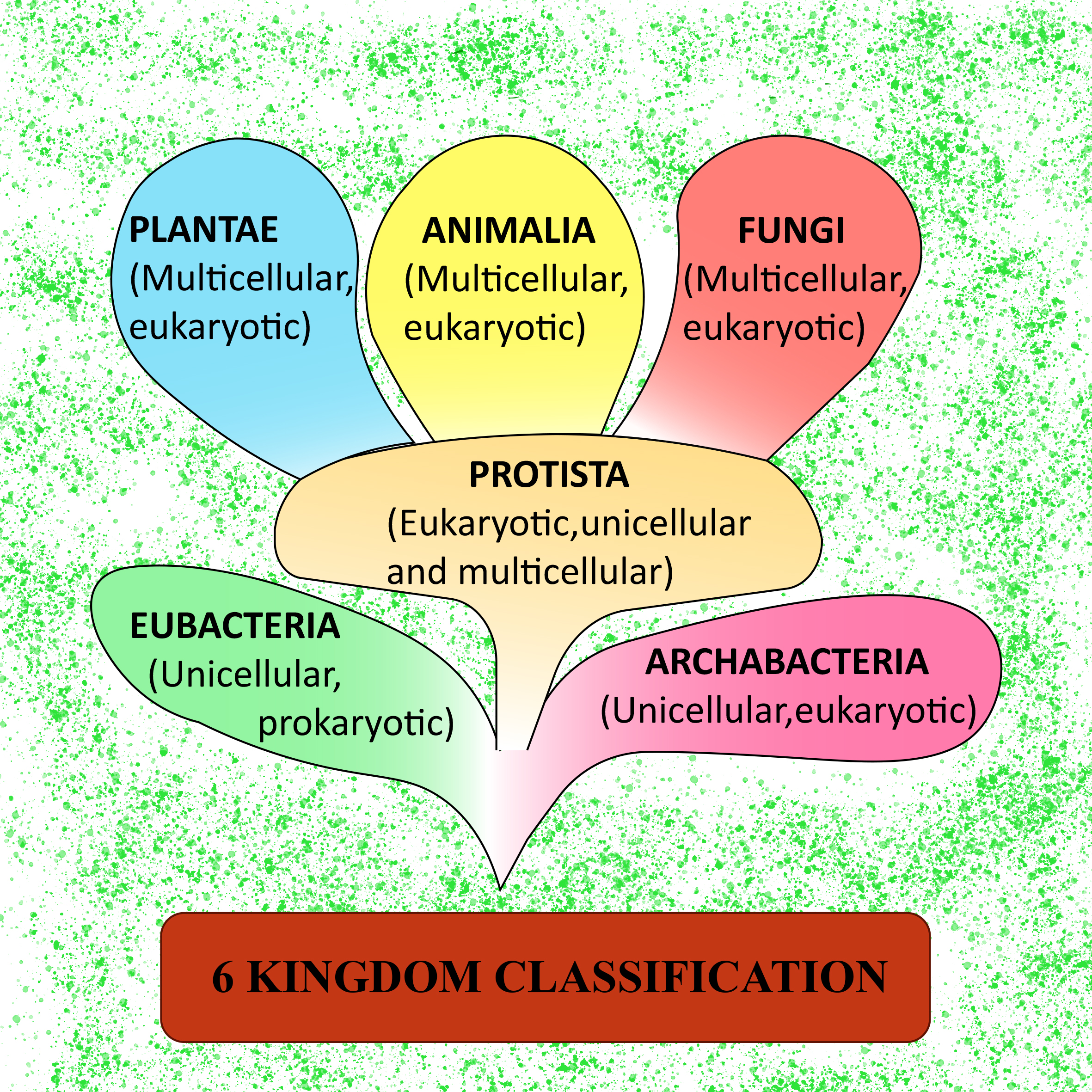
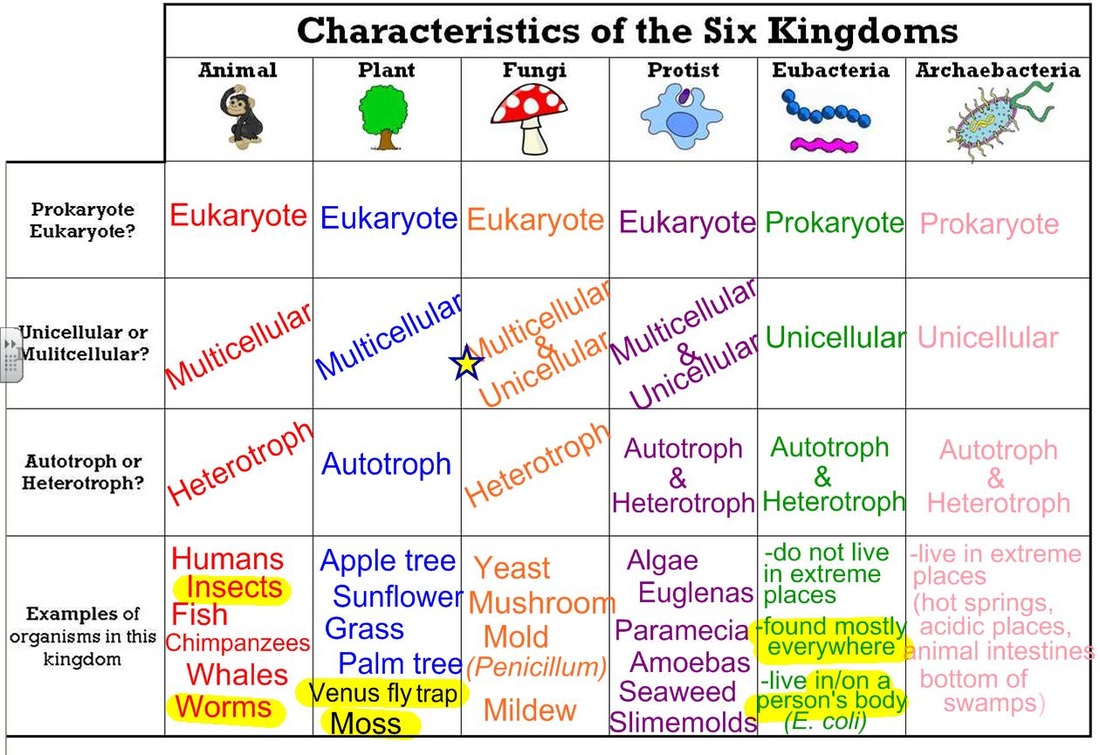
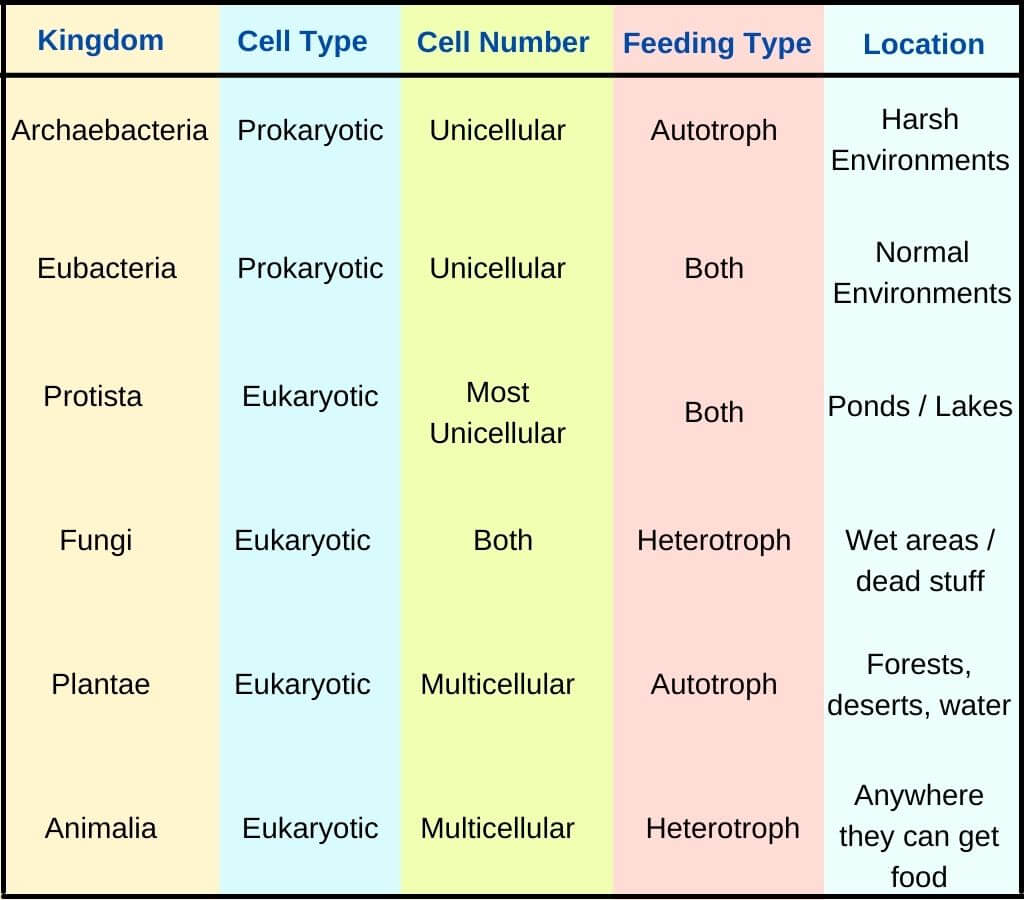
6 Kingdoms Chart - Web grade 06 science unit 11 pi 01. They are multicellular, eukaryotic organisms that are heterotrophic, meaning they obtain their energy by consuming other organisms. Archaebacteria, eubacteria, fungi, protista, plants and animals. Web 6 kingdoms of life, from simplest to most complex, are as follows: The organisms in each kingdom are considered biologically distinct from the others. Include basic characteristics, such as cell structure, the manner in which food is synthesized, and the mode of reproduction. The organisms are classified into their kingdoms by cell type (complex/simple), their ability to. Heffley, scott f created date: Well, they have some things in common. Web the 6 kingdoms kingdom: Bacteria, archaea, protista, plantae, fungi and animalia. Web the six kingdoms are: The organisms are classified into their kingdoms by cell type (complex/simple), their ability to. The chart below shows how the kingdoms have changed over time. Web the six kingdoms of life are animalia, plantae, archaebacteria, eubacteria, fungi and protista. Archaebacteria are unicellular organisms without a cell nucleus. Animal kingdom (animalia) there are lots of different kinds of animals, such as mammals, birds, insects, reptiles and amphibians. In biology, a kingdom of life is a taxonomy rank that is below domain and above phylum. Examples (give at last 3 specific examples of organisms in Archaebacteria, eubacteria, protista, fungi, plantae, or animalia. Heffley, scott f created date: Two separate charts that display the characteristics for the 6 kingdoms of life. Not making their own food as plants do. This kingdom includes all plants. Well, they have some things in common. So, why are so many diverse organisms in one kingdom? When there are 6 kingdoms, monera breaks into eubacteria and archaebacteria. Well, they have some things in common. Examples (give at last 3 specific examples of organisms in Web the 6 kingdoms kingdom: Examples (give at last 3 specific examples of organisms in The chart below shows how the kingdoms have changed over time. The organisms in each kingdom are considered biologically distinct from the others. Animalia, contains general animals and is the largest kingdom with over 1 000 000 species. These are animals, plants, fungi, protists, bacteria, and archaea. Web the 5 kingdoms of life are animalia, plantae, fungi, protista, and monera. When there are 6 kingdoms, monera breaks into eubacteria and archaebacteria. Prokaryote (lacks a nucleus) or eukaryote (has a nucleus)? Complete a semantic feature map to display the results of the. Animalia, contains general animals and is the largest kingdom with over 1 000 000 species. The organisms in each kingdom are considered biologically distinct from the others. So, why are so many diverse organisms in one kingdom? Web typically however, life is separated into six kingdoms: Plantae, contains all plants on earth. This kingdom includes all plants. These are animals, plants, fungi, protists, bacteria, and archaea. Include basic characteristics, such as cell structure, the manner in which food is synthesized, and the mode of reproduction. Archaebacteria, eubacteria, fungi, protista, plants and animals. A breakdown of kingdom biology. Web today all living organisms are classified into one of six kingdoms: The organisms are classified into their kingdoms by cell type (complex/simple), their ability to. The kingdom is the largest group of organisms. A breakdown of kingdom biology. Each kingdom includes a set of organisms that share similar characteristics. In biology, a kingdom of life is a taxonomy rank that is below domain and above phylum. Archaebacteria, eubacteria, fungi, protista, plants and animals. Animal kingdom (animalia) there are lots of different kinds of animals, such as mammals, birds, insects, reptiles and amphibians. The organisms are classified into their kingdoms by cell type (complex/simple), their ability to. Each kingdom includes a set of organisms that share similar characteristics. Animalia, contains general animals and is the largest kingdom. Classify organisms into their domain and kingdom by sorting cards with various organisms into the proper category. This kingdom includes all plants. Web the six kingdoms of life are animalia, plantae, archaebacteria, eubacteria, fungi and protista. Web the 5 kingdoms of life are animalia, plantae, fungi, protista, and monera. Web today all living organisms are classified into one of six. These are animals, plants, fungi, protists, bacteria, and archaea. The chart below shows how the kingdoms have changed over time. Heffley, scott f created date: Prokaryote (lacks a nucleus) or eukaryote (has a nucleus)? Web 6 kingdoms of life chart kingdom cell type body form cell structure nutrition habitat distinguishing characteristics examples animalia plantae fungi protista eubacteria archaebacteria. Animalia, contains general animals and is the largest kingdom with over 1 000 000 species. Well, they have some things in common. Archaebacteria are unicellular organisms without a cell nucleus. Web organisms are traditionally classified into six kingdoms (archaebacteria, eubacteria, protista, fungi, plantae, and animalia) based on characteristics like cell type, nutrient acquisition, and reproduction. A breakdown of kingdom biology. These are animals, plants, fungi, protists, bacteria, and archaea. Autotroph (producer) or heterotroph (consumer)? Web the 6 kingdoms kingdom: They are multicellular, eukaryotic organisms that are heterotrophic, meaning they obtain their energy by consuming other organisms. Web there are six kingdoms that all have different properties and vary widely. Web there are now six commonly accepted kingdoms. The kingdom is the largest group of organisms. Who couldnt find any good study material so decided to make her own. The organisms are classified into their kingdoms by cell type (complex/simple), their ability to. Web the 5 kingdoms of life are animalia, plantae, fungi, protista, and monera. In this activity, students will create a chart that describes each kingdom and provides examples of organisms that fall into that kingdom.A Simple Explanation of the 6 Kingdoms of Life
Diagram showing six kingdoms of life illustration Stock Vector Image
The Six Biological Kingdoms
Science poster of six kingdoms of life 2906732 Vector Art at Vecteezy
Information poster of six kingdoms of life 2906704 Vector Art at Vecteezy
Kingdom Biologi Homecare24
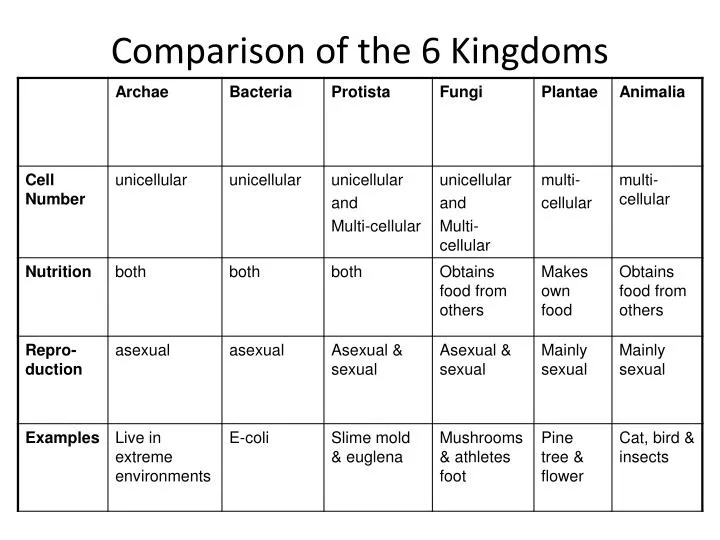
PPT Comparison of the 6 Kingdoms PowerPoint Presentation, free
Classification of Organisms Rumney Marsh Academy Science Revere
Montessori Materials The Six Kingdoms Chart with Cards
The 6 Kingdoms of Life Simple Explanation for Kids WeHaveKids
All Animals Can Move On Their Own.
Prokaryote (Lacks A Nucleus) Or Eukaryote (Has A Nucleus)?
Each Chart Shows The Following Characteristics:
Archaebacteria, Eubacteria, Protista, Fungi, Plantae, Or Animalia.
Related Post:

:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/six-kingdoms-of-life-373414-Final1-5c538e2446e0fb00013faa3c.png)